Should i take pqq with coq10?
In today’s fast-paced society, health has become an increasingly important factor that people cannot afford to ignore. Taking supplements to improve physical fitness and boost immunity has become more and more common. PQQ and CoQ10, as two powerhouse supplements in the industry, are often compared to each other.
What is PQQ?
PQQ (pyrroloquinoline quinone) is a vitamin-like substance that was discovered in 1979. Since the body cannot produce PQQ itself, it is believed that it may be a new vitamin. At the beginning of the 21st century, it was recognized as part of the vitamin B family.¹
Today, the substance is considered a cofactor in metabolism . PQQ is involved in important reactions, especially in the mitochondria. PQQ is also a so-called coenzyme in the body.

What is a coenzyme?
The term coenzyme means that the body uses this substance for a metabolic reaction and consumes it in the process. The reaction cannot take place without the coenzyme. It is part of an enzyme and an important aid for processes within the organism.

PQQ Effect: What does the coenzyme do for your body?
There are already more than 1,100 entries about PQQ on Pubmed, one of the largest research platforms for medicine. Popular search entries include “PQQ and mitochondria” and “PQQ and inflammation”.
To help you get an idea of the PQQ effect, we have put together some of the most important features for you - including the sources so that you can read the facts yourself at your leisure:
Strengthen mitochondria : PQQ can ensure that mitochondria grow in the body's cells and thus support energy production
Relieve inflammation: PQQ can promote the production of anti-inflammatory messengers and thus contribute to inflammation regulation²
Support respiratory chain: PQQ plays a role in energy metabolism
Aging better: PQQ can alleviate oxidative stress and thus possibly accompany the aging process
Provide energy: PQQ can renew coenzyme Q10 so that it can continue to function in energy production
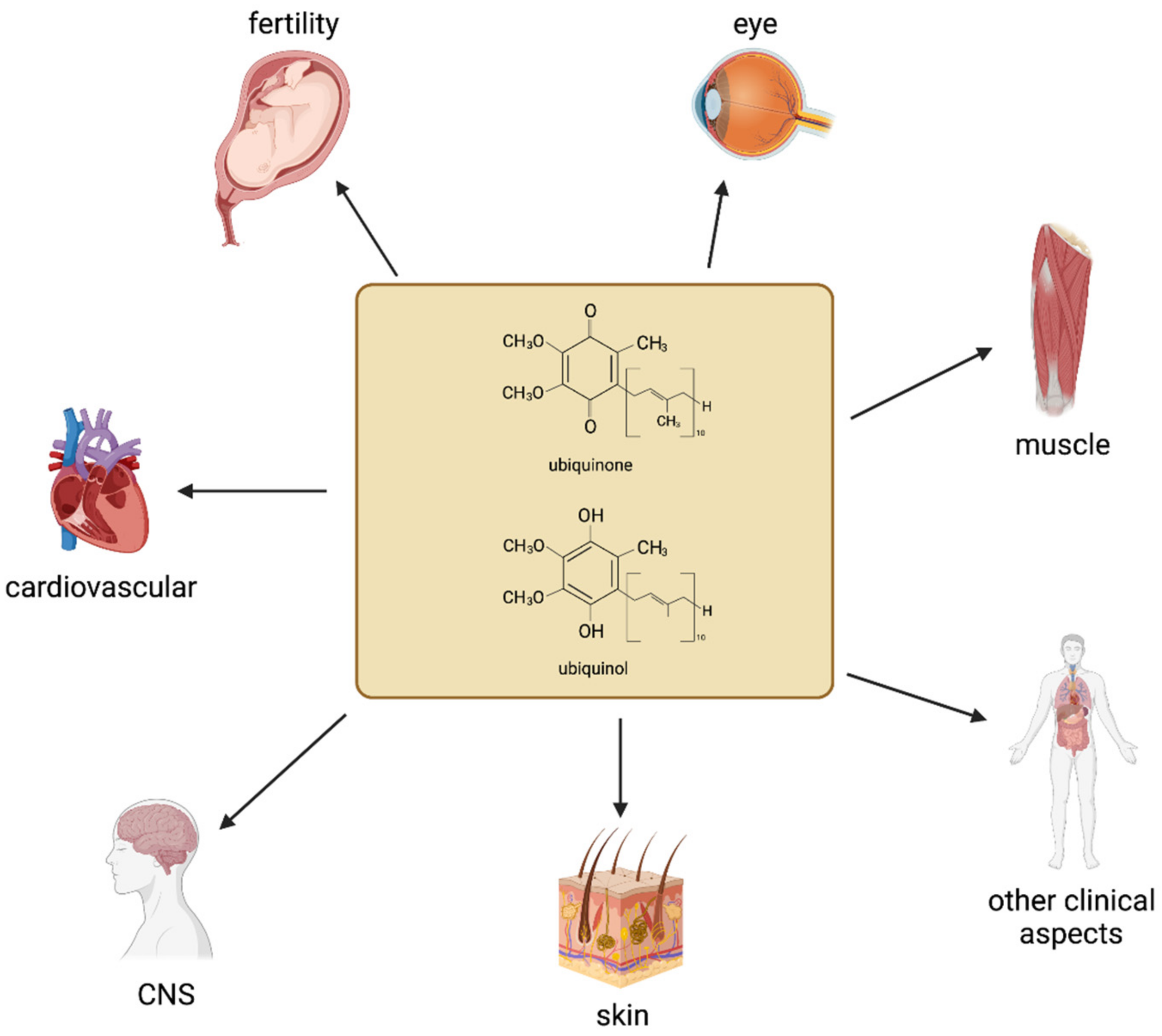
Function: What effect does coenzyme Q10 have on your well-being?
Q10 is found within cells mainly in the mitochondria. More precisely, the substance is located on the inner mitochondrial membrane. Like many other coenzymes, ubiquinol is involved in the respiratory chain and acts as an electron carrier.
Without coenzyme Q10, the mitochondria would not be able to do their job and the energy production taking place there could come to a standstill. This is because Q10 is at the beginning of the electron transfer chain. If there are problems at this point, things cannot continue and the body cannot produce enough energy.
Just like PQQ, the coenzyme is an important helper for your mitochondria, so that they can produce energy and give you power for your tasks. A coenzyme Q10 deficiency would have physical consequences.
What is PQQ Used for?
PQQ, short for Pyrroloquinoline Quinone, is a bioactive compound with multiple biological activities, and is also referred to as the “14th vitamin” in the global medical community. PQQ is widely found in microorganisms, plants, animals, and the human body, making it an essential nutrient. Its functions can be summarized as follows:
| Antioxidant | PQQ can help eliminate free radicals in the body to some extent, acting as an antioxidant and protecting organs such as the heart and liver from oxidative damage. |
| Nerve Protection | PQQ can protect the nervous system and is often effective in treating symptoms caused by brain fatigue, such as insomnia and vivid dreams. |
| Improved Memory | PQQ can improve neuronal damage caused by glucose deprivation, thus enhancing memory function. |
| Boosted Immunity | PQQ stimulates the activation and proliferation of immune cells, thereby enhancing the body’s immune system and increasing resistance to diseases. |
| Enhanced Metabolism | PQQ promotes metabolism to a certain degree, improving the body’s metabolic capabilities and assisting in the elimination of toxins from the body. |
What is CoQ10 Used for?
CoQ10,or coenzyme Q10, is a fat-soluble quinone compound that is widely present in living organisms. It is primarily found in the inner membrane of mitochondria and is a lipid-soluble compound similar in structure to vitamin K. Its functions can be summarized as follows:
| Supports Heart Health | CoQ10 is an essential component in energy production within heart cells. It helps improve heart contractility and output, lowers blood pressure, and protects the heart from oxidative stress damage. |
| Antioxidant | CoQ10 possesses powerful antioxidant properties, capable of scavenging oxygen free radicals and reducing oxidative stress damage to cells. This helps slow the aging process and prevent the onset of various chronic diseases. |
| Enhances Exercise Performance | CoQ10 increases ATP production within cells, providing more energy for physical activity, thus improving endurance and athletic performance. |
| Promotes Muscle Health | CoQ10 helps reduce muscle damage and recovery time, enhances muscle strength, and is especially important for individuals engaged in high-intensity physical activities. |
| Improves Cognitive Function | CoQ10 may be beneficial for enhancing cognitive function, including memory and attention. It is particularly significant for the prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. |
How does CoQ10 work with PQQ?
If CoQ10 works to improve the speed and efficiency, then PQQ assists by promoting the growth of mitochrondria and together they help your body produce more energy, faster. Think of the cellular energy production process like a train.
1) The train is at its original location and loaded with food and oxygen.
2) The train is sent to its final destination where your body will take the food and oxygen, and turn it into energy.
3) The train returns to its original location with energy which your body will use, and replace it with more food and oxygen. The process then repeats.
In this example, the train is your mitochondria or powerhouses responsible for the process of converting food and oxygen into ATP energy. CoQ10 is like a supercharger that improves the speed of the train. PQQ is like a construction company that is always working to add additional cars to your train. In summary, CoQ10 improves the speed of your energy production train, while PQQ is adding and building additional capacity to your train.
Together they offer an incredible one-two punch in boosting cellular energy production. While more research needs to be conducted on the effects of CoQ10 and PQQ taken together, studies conducted separately on each supplement show that they both have distinct benefits to cellular energy production, heart health and brain health.

Why Do I Need Both PQQ and CoQ10?
PQQ is a nootropic that supports memory, provides energy, protects the brain and aids mitochondria by increasing their numbers. CoQ10 ensures the mitochondria you do have are functioning at their best. If you have more mitochondria all operating with more “spark,” you could have more energy, healthier cells, and improved brain and body function.
Both PQQ and CoQ10 are related to mitochondria, so don’t they do the same thing? No, CoQ10 and PQQ are not the same. Rather, they support and enhance one another. They make each other better. Together they provide a greater benefit than if taken individually. There is a multiplier effect to combining these two powerful nootropics.

Conclusion
The combination of CoQ10 and PQQ offers a powerful tool for enhancing energy production, supporting cardiovascular health, boosting cognitive function, and promoting longevity. By protecting cells from oxidative damage and supporting mitochondrial function, these nutrients help maintain overall cellular health, which is crucial for aging gracefully and maintaining an active lifestyle.
For those looking to enhance their nutritional intake, considering supplements that combine CoQ10 and PQQ could be a beneficial addition to their health regimen.
References
deutsche-apotheker-zeitung.de/daz-az/2003/daz-19-2003/uid-9706
Harris, CB, Chowanadisai, W., Mishchuk, DO, Satre, MA, Slupsky, CM, & Rucker, RB (2013). Dietary pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) alters indicators of inflammation and mitochondrial-related metabolism in human subjects. The Journal of nutritional biochemistry, 24(12), 2076-2084.
Singh, A.K., Pandey, SK, Saha, G., & Gattupalli, N.K. (2015). Pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) producing Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) alleviates age associated oxidative stress and hyperlipidemia, and improves mitochondrial function in aging rats. Experimental gerontology, 66, 1–9.
Jonscher, KR, Chowanadisai, W., & Rucker, RB (2021). Pyrroloquinoline-Quinone Is More Than an Antioxidant: A Vitamin-like Accessory Factor Important in Health and Disease Prevention. Biomolecules, 11(10), 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11101441
Kumazawa, T., Sato, K., Seno, H., Ishii, A., & Suzuki, O. (1995). Levels of pyrroloquinoline quinone in various foods. The Biochemical journal, 307 (Pt 2)(Pt 2), 331–333.