When to take L-ergothioneine?
What Is Ergothioneine?
Ergothioneine (ERGO) is a unique, naturally occurring, sulfur-containing amino acid produced by mushrooms, yeast, and some types of bacteria. It is unique because it behaves much like a vitamin in humans. Vitamins are essential for humans to ingest because we cannot make them in the body, and they are required in critical chemical reactions. While not considered a vitamin (yet), the importance of ERGO to human cellular metabolism is evident because our bodies have a cell membrane protein that is specific to transporting ERGO into cells. The presence of this transport protein signifies that ERGO is a critical component of cellular function.
What Does Ergothioneine Do?
Once incorporated into cells, ERGO exerts several biological actions that protect and enhance cellular function, including acting as an antioxidant, inflammation regulator, and detoxification aid.
Emerging evidence shows that diets rich in ERGO exert these protective effects and promote longevity. For these reasons, ERGO has been referred to as the "longevity vitamin."

How Much L-ergothioneine Per Day Is Commonly Recommended?
Most experts and brands suggest 5 to 30 mg of L-ergothioneine per day, although no strict universal guideline exists. Individual factors—like diet, lifestyle stress, and health priorities—can tilt you toward the lower or higher end of the spectrum.

Can Higher Doses Offer More Benefits?
Exceeding typical ranges (like jumping to 50 mg or 100 mg daily) doesn’t necessarily yield multiplied benefits, and research on high-dose safety is still limited. Most experts suggest staying within moderate, proven ranges unless guided by a professional.
While L-ergothioneine is known for its powerful cell protection, each nutrient has a threshold beyond which your body’s active transport systems can’t use it efficiently. Since we have that specialized transporter (OCTN1) for L-ergothioneine, saturating it with extremely high doses might not yield a linearly higher effect. In other words, once the transporter is busy or you have enough to saturate your tissues, extra amounts could be excreted or simply not utilized as you’d hope.
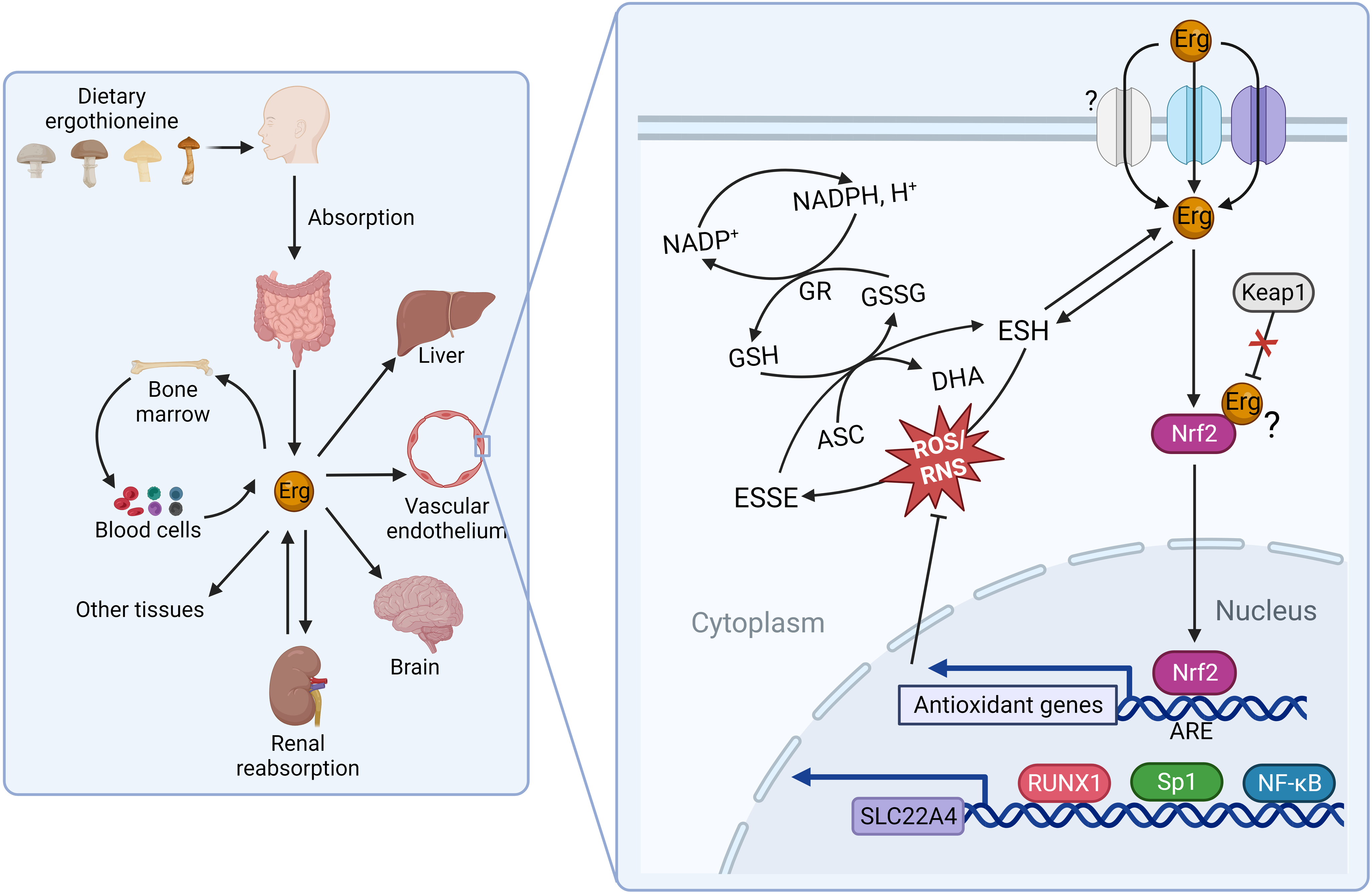
Are There Specific Groups Who Need More L-ergothioneine?
Those exposed to higher oxidative stress—athletes, older individuals, or those in polluted environments—may see greater benefits from slightly higher L-ergothioneine doses. While not mandatory, it can be a strategic addition for enhanced cellular resilience.
No two bodies are identical. One person might breeze through daily life with minimal stress, while another navigates night shifts, heavy workouts, or demanding city environments. Each lifestyle nuance can shape how much L-ergothioneine your body might actually need.
1. Older Adults
As we age, our natural antioxidant defenses can weaken. We produce fewer enzymes that neutralize free radicals, and cellular damage can accumulate. L-ergothioneine, with its stable, targeted antioxidant profile, could help buffer this decline. Older individuals often appreciate a moderate-to-higher daily dose—somewhere in the 15–30 mg range—to support healthy aging processes. They may also combine it with other age-focused nutrients, such as coenzyme Q10 or Ectoine for skin health. I’ve heard older friends say they feel a bit more “pep” in their step when they keep up a consistent L-ergothioneine habit, though that is, of course, anecdotal.
2. High-Stress Lifestyles
Got a stressful corporate job with 10-hour days and minimal downtime? Or do you hustle in a busy city with thick pollution? Chronic stress, poor air quality, and irregular sleep all ramp up oxidative stress in your system. If your diet is also patchy—like skipping balanced meals or ignoring fruits and veggies—your antioxidant reserves can dip. L-ergothioneine may help fill in the gap. People in these scenarios might choose daily intakes around 20 mg. When combined with a decent dose of vitamin C and a focus on better sleep, L-ergothioneine can help them feel less drained.
3. Athletes or Fitness Enthusiasts
Pushing your body in intense workouts or sports can yield impressive performance gains, but it also spikes oxidative stress. That’s part of the muscle adaptation process. Yet, chronic overtraining or lacking enough antioxidants can hamper recovery. Some sports nutrition experts suggest a moderate dose, like 15 mg or so, to assist muscle resilience. If you’re training for a marathon or triathlon, you might inch higher, up to 20–25 mg, especially during peak training cycles. However, it’s wise not to rely solely on L-ergothioneine—nutritional variety plus rest days matter too.

What Makes Ergothioneine Important?
Ergothioneine is a thiol
ERGO is a thiol, meaning it is a sulfur-containing compound. Some of its antioxidant and potential antiaging effects are similar to other thiol-containing compounds, such as glutathione and coenzyme Q10.
ERGO is different because it is a much smaller molecule distributed throughout the body and all the compartments of the cells, including the internal cellular environment (cytoplasm) and within mitochondria (the energy-producing compartment of cells).
A clinical study in humans has shown that taking ERGO as a dietary supplement raises blood levels of ERGO, improves thiol status, and may increase antioxidant status to produce various health benefits.
Vitamins are compounds in food without which we cannot live or be healthy. We cannot make them in our bodies, so they must be ingested.
With classic vitamins like vitamin A, B vitamins, and vitamin C, the identification of their importance to human health was discovered by the link between a dietary deficiency of the vitamin and a particular set of signs and symptoms of deficiency disease.
ERGO is different in that a deficiency state has not yet been identified because it is found in small quantities in all food. That low level probably keeps a severe deficiency from appearing, but it is far from optimal.
Ergothioneine levels in the body
Another factor that suggests how important ERGO is to human health is how efficient the human body is in concentrating and holding on to this compound. If ERGO were unimportant, it would not be concentrated and retained so efficiently.
In particular, body tissues highly active in energy metabolism and susceptible to oxidative stress and inflammation contain the richest concentration of ERGO. Specifically, the brain, liver, intestinal cells, testes, bone marrow, kidney, spleen, lung, and eyes. Tissues that ERGO is also found in higher concentrations in seminal fluid and breast milk. Again, all of this data indicates ERGO may be an essential vitamin.

How to Incorporate L-ergothioneine into a Daily Regimen?
L-ergothioneine is typically water-soluble and stable, so you can take it whenever it fits your routine—some prefer morning with breakfast, others pair it with midday or evening supplements. Consistency tends to matter more than timing, and synergy with other nutrients or a balanced meal may support optimal absorption.
Timing
While there’s no strict rule, I typically swallow my L-ergothioneine capsule with breakfast. Why? It pairs nicely with my other micronutrients, plus a meal can help overall absorption. L-ergothioneine doesn’t rely heavily on fat for absorption (unlike fat-soluble vitamins, e.g., A, D, E, K), but having some food in your stomach can reduce any slight GI discomfort if you’re sensitive.
Synergy
Do you take other antioxidants or functional ingredients? L-ergothioneine typically plays well with others. If you have a multi-ingredient formula—like a brain booster or an anti-aging blend—it might contain 5 mg of L-ergothioneine along with coenzyme Q10 or Nervonic Acid. Alternatively, you can layer it into your personal routine, ensuring you’re not doubling up unnecessarily.
Lifestyle Pairings
No supplement can outrun junk food or chronic stress, so think holistically. If you’re adding L-ergothioneine for extra antioxidant defense, also try including more colorful fruits and veggies, moderate exercise, and consistent sleep.
Ergothioneine as a Dietary Supplement
Taking supplemental ergothioneine may be a good option, given its safety and the possible health benefits of raising the intake of ERGO.
Regarding the safety of ERGO, it has undergone extensive studies to determine its safety. Even at extremely large doses, no adverse effects were seen in animal studies. And the recommended supplemental dosage level of 30 mg per day is well below the no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) of 800 mg per kg body weight per day established by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). ERGO has also been established as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
A human clinical trial verified the effectiveness of ERGO as a dietary supplement, showing that it is absorbed and retained in the body based upon increased levels of ERGO in the red blood cells (preferentially) and plasma, combined with minimal excretion in the urine (less than 4% of oral dosage). The increase in ERGO was associated with a downward trend in inflammation and oxidative damage biomarkers.

Conclusion
While ergothioneine naturally occurs in all foods, more than the general dietary intake may be required to provide optimal intake, especially in those who do not or cannot eat mushrooms regularly.
There are also some genetic variations among individuals where higher levels of dietary intake or supplementation may be indicated. In studies measuring blood levels of ERGO after consuming standardized intake levels of high ERGO mushrooms, the blood values varied more than ten-fold. Eventually, blood measurements, especially red blood cell levels of ERGO, may be used to ensure optimal ERGO intake.
For L- Ergothioneine Powder there are different specification for your choice, we can provide 10-30g of free samples, US warehouse in stock of 500kg of each month for the market of the global. certificate of analysis (COA), MSDS, specification sheet, pricing quotation is obtainable upon your request.
If you have any question or need any documents, welcome to contact us by e-mail: info@yanggebiotech.com