organic blue spirulina powder benefits
Spirulina is blue-green algae that’s packed with vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and protein. It has a long history as a superfood. First eaten by the ancient Aztecs for its nutrition, spirulina was used more recently as a supplement for NASA astronauts on space missions.
Today, research supports many of the potential benefits of spirulina, and researchers continue to study its potential for treating health concerns. Spirulina is available in powder, capsule, and tablet forms, and it’s added to certain protein bars, smoothies, and juices.
What is it?
Blue Spirulina powder is a blue-green algae that is extracted from Green Spirulina and it is a very great source of antioxidants. It is a common misconception that it is also is a source of protein and a range of nutrients and vitamins, including B1, B2, B3, B6, and B9, as well as Vitamin C, Vitamin A, Vitamin D, and E. But in fact, these are the qualities of Green Spirulina.\

Spirulina Nutrition Information
One tablespoon of spirulina contains:
- Calories: 20
- Protein: 4 grams
- Fat: 1 gram
- Carbohydrates: 2 grams
- Fiber: 0 grams
- Sugar: 0 grams
Spirulina is a good source of:
- Thiamine (vitamin B1)
- Riboflavin (vitamin B2)
- Niacin (vitamin B3)
- Copper
- Iron
Spirulina also contains magnesium. This mineral supports normal daily functions like muscle movements and your heartbeat. It’s also responsible for producing protein and creating energy – but most people don’t get enough in their diet.
Potential Health Benefits of Spirulina
Spirulina is a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids. It’s also high in the plant protein phycocyanin, which has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
These nutrients in spirulina are linked to several health benefits:
Anti-cancer properties
Many antioxidants in spirulina have anti-inflammatory effects in the body. Chronic inflammation contributes to cancer and other diseases.
Phycocyanin has been found to not only reduce inflammation in the body, but also block tumor growth and kill cancer cells. The immune-enhancing protein is being studied for its potential in cancer treatment.
Heart health
Research has found that the protein in spirulina can reduce your body’s absorption of cholesterol, lowering cholesterol levels. This helps keep your arteries clear, reducing strain on your heart that can lead to heart disease and stroke-causing blood clots.
Phycocyanin also reduces triglyceride levels. These are fats in your blood that can contribute to the hardening of arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and pancreatitis.
Spirulina increases nitric oxide production in your body as well, which helps your blood vessels relax. Studies show that this can reduce yourblood pressure, lowering your heart disease risk.
Allergy relief
The anti-inflammatory effect of spirulina’s antioxidants may help you withallergies caused by pollen, animal hair, and dust. One study found that symptoms likecongestion, sneezing, and itching were reduced significantly, suggesting that spirulina may be a good alternative to allergy medications.
Immune system support
Spirulina is rich in a range of vitamins and minerals essential for maintaining a healthy immune system, like vitamins E, C, and B6. Research finds that spirulina also boosts the production of white blood cells and antibodies that fight viruses and bacteria in your body.
Laboratory studies show that spirulina can fight herpes, the flu, and HIV – though much more research is needed to test these effects in humans.
Eye and oral health
Spirulina is concentrated with zeaxanthin, a plant pigment that may reduce the risk of cataracts and age-related vision loss. Its antibacterial properties may also help promote good oral health. One study found that spirulina-enhanced mouthwash reduced dental plaque and the risk of gingivitis in the people being studied. Another study showed it lowered the risk of oral cancer in people who chew tobacco.
Weight loss
Spirulina is a source of protein, which takes longer for your body to digest and can fend off hunger. One study done on people on a low-calorie diet found that those who took a spirulina supplement shed more weight and lost more body fat, compared to those who had a placebo pill. Spirulina may also help you feel fuller and prevent fat buildup in the liver, both of which also encourage weight loss.

Risks and Side Effects
Blue spirulina is generally considered safe for consumption when used in appropriate amounts. However, as with any food or dietary supplement, there are a few potential risks and side effects to be aware of, including the risk of an allergic reaction and potential digestive issues, such as stomach cramps, nausea or diarrhea.
It’s also important to be aware that if blue spirulina is not sourced from reputable suppliers or processed under proper conditions, there is a risk of contamination with harmful substances such as heavy metals or microorganisms. To minimize this risk, it’s important to purchase blue spirulina from trusted sources.
Blue spirulina may interact with certain medications, such as immunosuppressants or anticoagulants. If you’re taking any medications or have underlying health conditions, consult with a health care professional before incorporating blue spirulina into your diet.
Also, exercise caution before using it if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
How to Add Spirulina to Your Diet
Experts recommend taking no more than 8 grams of spirulina a day. That’s a little more than two teaspoons of the blue-green algae. You can use it in the following ways:
Spirulina powder
Try adding the powder to guacamole, hummus, or pesto. You can also sprinkle it on popcorn and salads, or mix it into energy balls or granola bars. Spirulina has an earthy, fishy flavor that some people may find off-putting.
Spirulina tablets
If you don’t like the taste of spirulina, a tablet or capsule may work for you.
Adding spirulina to drinks
Spirulina adds nutrients to any smoothie. You can also stir spirulina powder into juice; the sweetness can mask the flavor.
Is spirulina safe for everyone?
Those with the condition called phenylketonuria (PKU) should avoid spirulina completely as it contains an amino acid called phenylalanine, which those with this condition cannot metabolise. Anyone with an autoimmune condition such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus or multiple sclerosis should also avoid spirulina.
Others who should check with their GP before taking spirulina include those taking prescription medication, pregnant or breastfeeding women, and anyone younger than 18.

Conclusion
Spirulina is a type of cyanobacteria — often referred to as blue-green algae — that is highly nutritious.
Studies show that it may improve cholesterol and triglyceride levels, suppress oxidation, reduce blood pressure, and lower fasting blood sugar levels. However, more research is needed.
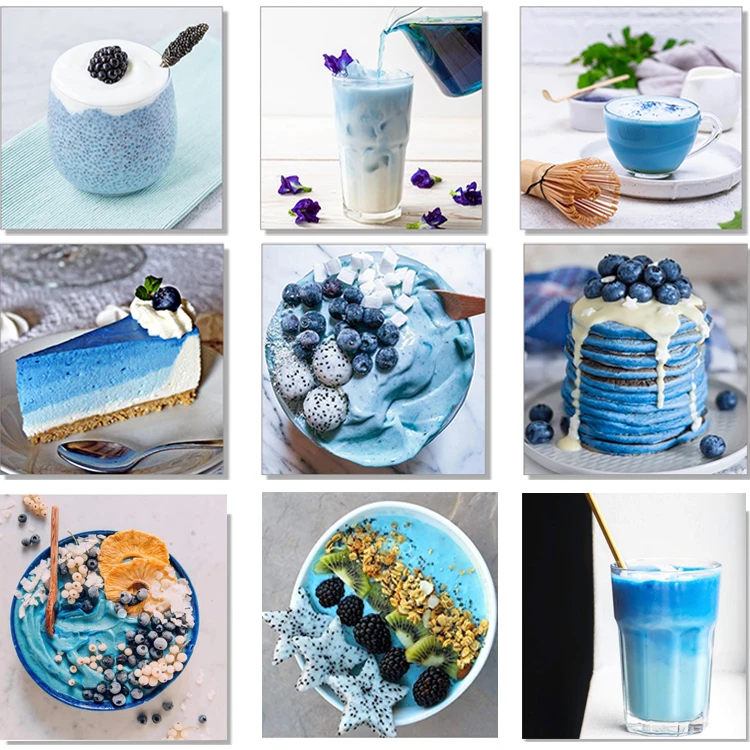
Blue spirulina is a natural extract derived from certain species of blue-green algae, particularly Arthrospira platensis. It’s a vibrant blue colour, making it a popular ingredient in the food and beverage industry, as well as in health and wellness products.
Blue spirulina is rich in antioxidants and some immune-boosting micronutrients, including vitamin C and vitamin E. It may also promote muscle recovery, and some studies suggest it may have anti-cancer properties.
The colorant is largely used in the culinary world to add a bright blue color to baked goods, desserts and other dishes. When using it, start with a small amount (about ¼ teaspoon), and increase as needed.
Spirulina FAQs
What does spirulina do to the body?
Because spirulina is high in nutrients and antioxidants, it may help lower inflammation in the body. It may improve your immune system and heart health, and reduce the risk of several diseases.
Is spirulina safe to take every day?
Spirulina is considered safe, even in high doses. Experts recommend getting no more than 8 grams per day.
What foods is spirulina found in?
Spirulina is a type of algae. It’s sometimes added to certain foods and beverages, such as smoothies, popcorn, and energy bars.
Is spirulina good for you to lose weight?
Spirulina is low in calories and high in protein, which can help you feel full and fend off hunger. Research suggests that it may encourage weight loss.
References:
The Guardian: “Spirulina: a luxury health food and a panacea for malnutrition.”
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition: “Vitamin B-12 from algae appears not to be bioavailable.”
Cardiovascular Therapeutics. “Hypolipidemic, Antioxidant and Antiinflammatory Activities of Microalgae Spirulina.”
Cleveland Clinic: “3 Vitamins That Are Best for Boosting Your Immunity,” “7 Foods That Are High in Magnesium.”
Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology: “Nutritional and Therapeutic Potential of Spirulina.”
Current Protein & Peptide Science: “C-phycocyanin: a biliprotein with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects.”
ESHA Research Inc., Salem, OR: “Spirulina.”
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology: “The effects of spirulina on allergic rhinitis.”
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences: “Effects of spirulina consumption on body weight, blood pressure, and endothelial function in overweight hypertensive Caucasians: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial.”
Free Radical Biology and Medicine: “Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked?”
International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences: “Effectiveness of spirulina mouthwash on reduction of dental plaque and gingivitis: a clinic study.”
Journal of Cancer: “Phycocyanin: A Potential Drug for Cancer Treatment.”
Journal of Infection and Public Health: “Spirulina consumption effectively red
Send Inquiry
Related Industry Knowledge
- Amazing Benefits of the Milk Thistle to Liver
- Wheatgrass powder
- Blueberry Extract Benefits for Skin
- Organic Turmeric with Black Pepper Health Benefits
- What is Glutathione and Why Do We Need it?
- Benefits of Chlorella Tablets: Skin and Hair
- Benefits of Turmeric and Black Pepper Capsules
- The amazing skincare benefits of matcha for all skin types
- What Does Creatine Do and Why You Should Use It for Muscle Growth
- What Are Exosomes Used for In Skincare