Liposomal creatine vs creatine monohydrate
Creatine is a well-known supplement in the fitness and sports industry, praised for its ability to enhance performance, increase muscle mass, and improve strength. Among the various forms of creatine available on the market, Creatine Monohydrate and Liposomal Creatine are two popular choices. This article delves into the differences between these two forms, examining their efficacy, absorption rates, and overall benefits to help you make an informed decision.
What Is Creatine and Why Does It Matter?
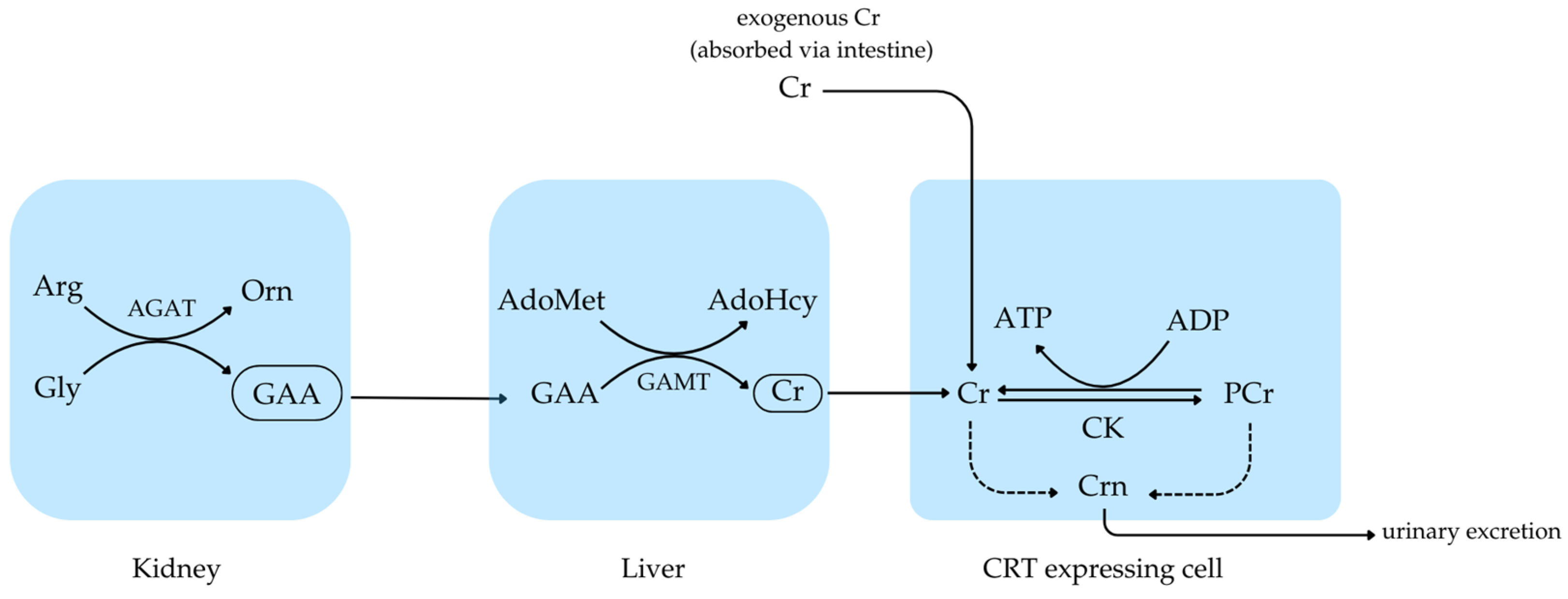
Creatine is a naturally occurring, mostly muscle-specific amino acid, which is composed of the amino acids arginine, glycine and methionine. It is necessary for making adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the major source of energy for fast, short-term movements like sprinting, lifting weights and other explosive activities. Around 95 per cent of creatine in the body is locked up in muscle where it binds to phosphates and becomes phosphocreatine (PCr). During intense physical activity, phosphocreatine replenishes ATP, which is quickly used up in muscle contractions. Creatine boosts phosphocreatine stores and speeds up ATP replenishment, strength, power and recovery in high intensity training.

Structural chemical formula of creatine. (BOC Sciences Authorized)
What is Creatine Monohydrate?
Creatine Monohydrate is the most researched and commonly used form of creatine. It consists of a creatine molecule bound to a water molecule and is known for its effectiveness and affordability. Creatine Monohydrate has been shown to:
Enhance muscle mass
Improve strength and power output
Boost recovery between exercise sets
Enhance cognitive function

What is Liposomal Creatine?
Liposomal Creatine is a newer form of creatine that is encapsulated within liposomes. Liposomes are tiny, spherical vesicles that can be filled with drugs or supplements, designed to improve the delivery and absorption of their contents. The theory behind Liposomal Creatine is that the liposomal encapsulation can:
Enhance absorption and bioavailability
Reduce gastrointestinal discomfort
Provide a sustained release of creatine
Improve cellular uptake

Applications of Liposomal Creatine
Liposomal creatine has garnered attention due to its enhanced bioavailability and efficient absorption. As a result, it has found various applications in sports, fitness, cognitive enhancement, and even age-related health maintenance. Below are some of the key applications where liposomal creatine has proven beneficial.
1. Athletic Performance: Liposomal creatine enhances ATP production, benefiting athletes in high-intensity sports like weightlifting and sprinting. Its improved absorption leads to better endurance, strength, and quicker recovery during intense workouts.
2. Muscle Mass and Strength Gains: For bodybuilders, liposomal creatine boosts muscle protein synthesis and supports muscle growth. Its efficient absorption promotes sustained strength and muscle development, with minimal side effects like water retention.
3. Cognitive Function Enhancement: Creatine also supports cognitive performance by aiding ATP production in the brain. Liposomal creatine improves focus, memory, and mental clarity, making it valuable for students and professionals.
4. Age-Related Muscle Loss: Liposomal creatine helps combat sarcopenia (muscle loss due to aging) by maintaining muscle mass and strength. Its improved absorption is particularly beneficial for older adults in preserving muscle function.
5. Rehabilitation and Recovery: Liposomal creatine speeds up recovery by supporting muscle repair and reducing breakdown after intense exercise or injury. It aids in muscle regeneration and shorter recovery times.
6. Enhanced Endurance: While typically used for strength, creatine can also benefit endurance athletes. Liposomal creatine helps delay fatigue, supporting longer performance during endurance events.
7. Fat Loss and Metabolic Support: Liposomal creatine may indirectly support fat loss by boosting muscle mass, increasing metabolism, and improving exercise performance, aiding in lean body composition.
8. Chronic Fatigue and Stress Management: By improving ATP production, liposomal creatine combats chronic fatigue and stress, enhancing recovery from physical and mental exertion.
Liposomal creatine, with its superior bioavailability, has shown wide application potential in many research fields. Whether it is research on sports performance, aging, rehabilitation, cognition and other fields, liposomal creatine provides more support for research in related fields through efficient absorption and targeted delivery. With further research, liposomal creatine may play a role in more health and performance enhancement, becoming an important tool for future sports science and biomedical research.

Comparing Absorption and Bioavailability
One of the main differences between Liposomal Creatine and Creatine Monohydrate lies in their absorption rates and bioavailability. Creatine Monohydrate is absorbed relatively well by the body, but some individuals may experience gastrointestinal issues or suboptimal absorption. Liposomal Creatine aims to address these concerns by providing a more efficient delivery system.
Studies on liposomal delivery systems suggest that they can protect the active ingredient from degradation in the digestive system and enhance uptake by cells. However, research specifically on Liposomal Creatine is limited, and more studies are needed to confirm its superiority over Creatine Monohydrate in terms of absorption and bioavailability.
Efficacy in Enhancing Performance
The primary reason for using creatine supplements is to improve athletic performance. Creatine Monohydrate has a proven track record, with numerous studies supporting its effectiveness in increasing strength, power, and muscle mass. Liposomal Creatine is believed to offer the same benefits, but due to its relatively recent introduction to the market, there is less scientific evidence available.
Until more research is conducted, it’s difficult to definitively state whether Liposomal Creatine is more effective than Creatine Monohydrate in enhancing performance. However, the potential for improved absorption could suggest benefits for those who have not responded well to Creatine Monohydrate in the past.
Side Effects and Tolerability
Both forms of creatine are generally considered safe when used as directed. Creatine Monohydrate may cause side effects such as bloating, water retention, and gastrointestinal distress in some users. Liposomal Creatine is marketed as a gentler option, potentially reducing these side effects due to its encapsulation.
It’s important to note that individual responses to creatine supplements can vary, and what works well for one person may not work for another. Monitoring your body’s reaction to different forms of creatine is key to finding the most suitable option.
Effectiveness for Muscle Strength & Performance
Creatine Monohydrate
Creatine monohydrate has been the industry standard for decades, and for good reason. It is the most researched form of creatine, with hundreds of clinical studies confirming its ability to enhance strength, power output, and muscle mass. Its effectiveness stems from its ability to increase phosphocreatine stores in the muscles, which are crucial for the rapid regeneration of ATP, the body’s main energy currency during high-intensity activities.
By elevating ATP availability, creatine monohydrate helps athletes perform more repetitions, lift heavier weights, and maintain higher training intensity. Over time, this leads to significant improvements in muscle hypertrophy, explosive strength, and overall performance. Its long-standing success in sports nutrition makes it the most trusted and validated option for maximizing physical output.
Liposomal Creatine
Liposomal creatine is a newer innovation designed to deliver the same performance-enhancing effects as monohydrate—but with improved efficiency. By encapsulating creatine within phospholipid “liposomes,” this form protects the molecule from degradation in the stomach and enhances its transport across the intestinal wall. As a result, more creatine is believed to reach the bloodstream intact.
Because of this improved absorption, liposomal creatine may help users achieve effective muscle saturation levels more quickly, even with smaller doses. Enhanced bioavailability could also support more consistent creatine levels throughout the day, potentially contributing to smoother energy output and steadier training performance.
Although research is still emerging, early evidence and biochemical logic suggest that liposomal creatine can deliver similar—or potentially superior—performance benefits compared to monohydrate, especially for individuals with poor digestive tolerance or limited nutrient absorption.
Which One Should You Choose?
1. For proven effectiveness and value: Creatine monohydrate is the most studied, proven, and cost-effective choice for most people.
2. For potential reduction in water retention: If you are concerned about water retention and are willing to pay a premium, liposomal creatine might be a good option to try, but be aware that scientific backing for its superiority is limited.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both Liposomal Creatine and Creatine Monohydrate have their own set of advantages and potential drawbacks. Creatine Monohydrate is backed by extensive research and is known for its cost-effectiveness, while Liposomal Creatine promises improved absorption and tolerability, albeit at a higher cost and with less scientific evidence.
The decision between the two should be based on individual goals, budget, and response to supplementation. It’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Send Inquiry
Related Industry Knowledge
- Blue Spirulina E10: Nature’s Blue Superfood
- Plant Carbon Black: Revolutionizing the Rubber Industry
- Turmeric with Black Pepper: Ginger Benefits
- What is Broccoli Extract Powder Benefits?
- How Can Hyaluronic Acid Powder Improve Skin?
- What is the benefit of liposomal glutathione?
- Laminaria Digitata Extract for Fat Loss & Metabolism Boost
- What are the benefits of black carrots powder?
- What are the medicinal benefits of Cordyceps militaris powder?
- Lycopene as an antioxidant