Is beta-carotene coloring safe?
Color plays an essential role in the way we perceive food and beverages. Bright, vibrant colors are often associated with freshness, quality, and taste appeal. This is why food manufacturers rely heavily on food colorings—both natural and synthetic—to enhance product appearance. Among these, beta-carotene (E160a) stands out as one of the most widely used natural colorants, lending foods a warm yellow to deep orange hue.
Beyond aesthetics, beta-carotene is also valued for its nutritional role as a precursor of vitamin A, a vital nutrient for vision, immune function, and skin health. But with increasing awareness of food additives and their impact on health, many consumers often ask: Is beta-carotene coloring safe?
In this blog, we’ll take a deep dive into what beta-carotene is, its function in the body, its role as a food colorant, regulatory evaluations, potential risks, and why it remains one of the safest and most beneficial natural food colorings available.
What Is Beta-Carotene?
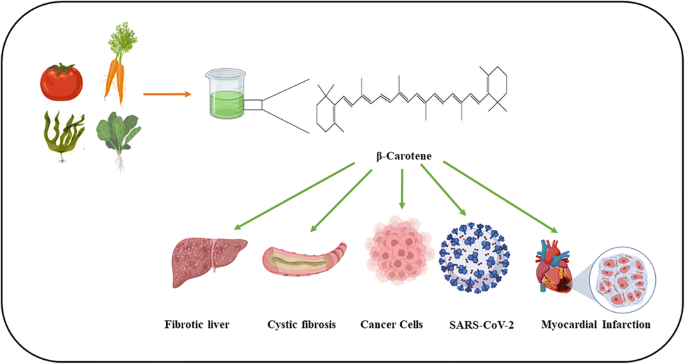
Beta-carotene is a naturally occurring carotenoid—a group of pigments responsible for the bright red, orange, and yellow colors in many fruits and vegetables. Carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkins, and leafy greens are rich sources of this pigment.
Chemically, beta-carotene is a provitamin A compound, meaning the body can convert it into vitamin A (retinol) as needed. Unlike preformed vitamin A found in animal sources (like liver), which can be toxic at high levels, beta-carotene’s conversion is self-regulated—preventing the risk of vitamin A toxicity from food sources.
In the food industry, beta-carotene is either:
-
Extracted naturally from plants such as carrots or algae (Dunaliella salina), or
-
Produced synthetically to ensure consistent quality and stability.
When used as a food additive, it is labeled as E160a in the EU and is approved worldwide as both a nutrient and a coloring agent.
Why Is Beta-Carotene Used as a Coloring Agent?
The demand for natural colorants has been growing, as consumers increasingly seek “clean-label” products free from artificial dyes. Beta-carotene is favored because:
-
Natural Appeal: It is derived from recognizable plant sources.
-
Bright and Stable Color: Provides a consistent yellow to orange tone, ideal for beverages, dairy, margarine, and bakery goods.
-
Dual Functionality: It not only colors food but also acts as a source of vitamin A.
-
Health Benefits: Its antioxidant properties make it more appealing than synthetic dyes.
Industries use beta-carotene in:
-
Margarine and butter
-
Soft drinks, juices, and energy drinks
-
Processed cheese and dairy products
-
Bakery and confectionery
-
Dietary supplements
Is Beta-Carotene Coloring Safe?
Regulatory StatusThe safety of beta-carotene has been extensively studied for decades. Major regulatory bodies have consistently confirmed its safety when used as intended:
-
FDA (U.S.): Lists beta-carotene as GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) for use in food and beverages.
-
EFSA (European Union): Approved as food additive E160a with an acceptable daily intake (ADI) of 0.03 mg/kg body weight per day (from all sources, including supplements).
-
WHO/FAO JECFA: Concluded beta-carotene is safe as a coloring and nutrient supplement.
Beta-Carotene and the Human Body
-
Vision Support – Beta-carotene is converted into vitamin A, which is crucial for the production of rhodopsin, a protein in the eyes that helps with low-light vision.
-
Immune Function – Vitamin A derived from beta-carotene supports healthy immune responses, helping the body fight infections.
-
Skin and Cellular Health – Acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative stress, slowing skin aging, and supporting wound healing.
-
Cancer Prevention (Potential) – Some studies suggest that diets high in beta-carotene-rich foods may reduce the risk of certain cancers, though supplementation studies have shown mixed results.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While beta-carotene is safe in food coloring amounts, certain considerations are worth noting:
1. Carotenemia (Harmless Condition)
Excessive intake of beta-carotene from foods can sometimes cause the skin to develop a yellow-orange tint, especially in children. This condition, called carotenemia, is harmless and reversible when intake is reduced.
2. High-Dose Supplements in Smokers
Some large-scale studies, including the ATBC Study (Alpha-Tocopherol Beta-Carotene Cancer Prevention Study), found that high-dose beta-carotene supplements increased lung cancer risk among heavy smokers. However, this applies to concentrated supplements, not food coloring or natural dietary intake.
3. Stability Concerns in Food Processing
Beta-carotene is sensitive to heat, oxygen, and light, which can cause degradation. Food manufacturers address this by using stabilized formulations.
Compared to artificial food dyes such as tartrazine (E102) or sunset yellow (E110), beta-carotene has clear advantages:
-
Natural Origin: Plant-based or bioengineered, versus petroleum-derived.
-
Nutritional Value: Provides provitamin A and antioxidant activity.
-
Safety Profile: Fewer allergic or hypersensitivity reactions compared to synthetic dyes.
-
Consumer Preference: Fits the “clean-label” trend.

Industrial Applications of Beta-Carotene Coloring
-
Food and Beverage Industry – Widely used in drinks, margarine, cheese, bakery, and confectionery.
-
Nutraceuticals – Used in dietary supplements for eye health, skin care, and immunity.
-
Cosmetics – Beta-carotene is added to skincare and cosmetic products for its antioxidant and color properties.
-
Pharmaceuticals – Incorporated in capsules and syrups as a coloring and nutrient.
Sustainability and Production
Natural beta-carotene is often derived from carrots or algae (like Dunaliella salina). Advances in biotechnology now allow production through fermentation and microalgae cultivation, reducing environmental impact. Both synthetic and natural forms are approved for use, with the natural form being preferred in organic or clean-label products.
FAQs on Beta-Carotene Coloring
1. Can children safely consume foods with beta-carotene coloring?
Yes. Beta-carotene is safe for children within recommended intake levels. Overconsumption may cause temporary carotenemia but no long-term harm.
2. Is beta-carotene coloring safe during pregnancy?
Yes. Beta-carotene is safe and even beneficial in pregnancy as it supports vitamin A needs without the toxicity risk of preformed vitamin A.
3. Does beta-carotene cause allergies?
Allergic reactions to beta-carotene are extremely rare, making it a safer alternative to some synthetic dyes.
4. Is there a difference between natural and synthetic beta-carotene coloring?
Both are safe and approved, but natural sources are often preferred for marketing and consumer perception.
Conclusion
Beta-carotene coloring stands out as one of the safest and most beneficial food colorants available today. Not only does it enhance the visual appeal of food and beverages, but it also provides essential nutritional and antioxidant benefits. Regulatory bodies worldwide, including the FDA, EFSA, and WHO, confirm its safety for human consumption within approved limits.
While extremely high-dose supplements may pose risks for certain populations (like heavy smokers), beta-carotene as a food coloring (E160a) is safe, well-tolerated, and aligned with the demand for natural, health-conscious ingredients.
As consumers continue to seek clean-label and functional foods, beta-carotene will remain a preferred choice for food manufacturers, balancing safety, nutrition, and sustainability.
You can bulk beta carotene powder at YANGGEBIOTECH company is an industry-leading manufacturer and distributor for pure dietary supplements. yanggebiotech.com is not just a consumer brand. It also supplies pure ingredients to other brands that distribute food and other supplement products. Contact yanggebiotech.com to place an order today.