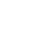
Is beta carotene an antioxidant?
When it comes to nutrition and wellness, antioxidants often take the spotlight. They are praised for their ability to combat free radicals, support healthy aging, and protect against chronic diseases. Among these powerful compounds is beta-carotene, a naturally occurring pigment that gives fruits and vegetables their vibrant orange, red, and yellow colors. But many people still ask: Is beta-carotene really an antioxidant?
The short answer is yes—beta-carotene is one of the most important antioxidants found in nature, but its role extends beyond that. It also serves as a precursor to vitamin A, an essential nutrient for vision, immunity, and skin health. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what makes beta-carotene an antioxidant, how it works in the body, and why it is so beneficial for your overall health. Yangge Biotech supply high quality beta carotene powder and extracts contact us for inquiries!
What is Beta-Carotene?
Beta-carotene is a carotenoid, a class of plant-based compounds responsible for the rich pigmentation in foods like carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkins, and leafy greens. It belongs to the group of provitamin A carotenoids, which means the body can convert it into retinol (vitamin A) when needed.
This dual function—serving as both an antioxidant and a vitamin A precursor—makes beta-carotene particularly unique. Unlike preformed vitamin A (found in animal products), which can accumulate and become toxic at high levels, beta-carotene conversion is regulated by the body, reducing the risk of toxicity.
How Does Beta-Carotene Act as an Antioxidant?
To understand beta-carotene’s antioxidant role, we need to first look at oxidative stress.
-
Free radicals are unstable molecules produced naturally in the body through metabolism, but their levels increase with environmental exposures such as smoking, pollution, and UV radiation.
-
When free radicals overwhelm the body, they damage DNA, proteins, and cell membranes—a process called oxidative stress.
-
Over time, oxidative stress contributes to aging, inflammation, and diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Beta-carotene’s antioxidant role comes into play here. As a carotenoid, it can neutralize free radicals, especially singlet oxygen (a highly reactive oxygen species). This prevents chain reactions that would otherwise damage cells and tissues.
In simpler terms: beta-carotene sacrifices itself to protect your cells from oxidative harm.
Scientific Evidence of Beta-Carotene’s Antioxidant Properties
Numerous studies highlight beta-carotene’s antioxidant potential:
-
Cellular Protection – Research shows beta-carotene protects lipids (fats in cell membranes) from peroxidation, reducing the risk of cell damage.
-
Cancer Research – Some studies suggest diets high in beta-carotene-rich foods may reduce the risk of certain cancers due to its antioxidant effects, though supplementation results vary.
-
Skin Defense – Beta-carotene accumulates in the skin and acts as a natural shield against UV radiation, reducing sun damage and premature aging.
-
Eye Health – Its antioxidant action helps protect the retina and lens from oxidative stress, lowering the risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).

Beta-Carotene and Vitamin A: A Dual Benefit
What sets beta-carotene apart from many other antioxidants is its ability to convert into vitamin A. Vitamin A is vital for:
-
Vision: It plays a key role in forming rhodopsin, the pigment in the retina that allows us to see in low light.
-
Immune Function: Vitamin A strengthens immune defenses by supporting the development of white blood cells.
-
Skin and Mucous Membranes: It helps maintain the integrity of epithelial tissues, keeping skin healthy and resilient.
This dual function means that by consuming beta-carotene-rich foods, you’re not just getting antioxidant protection—you’re also supplying your body with a critical nutrient.
Health Benefits of Beta-Carotene as an Antioxidant
Here are some of the most notable ways beta-carotene contributes to health:
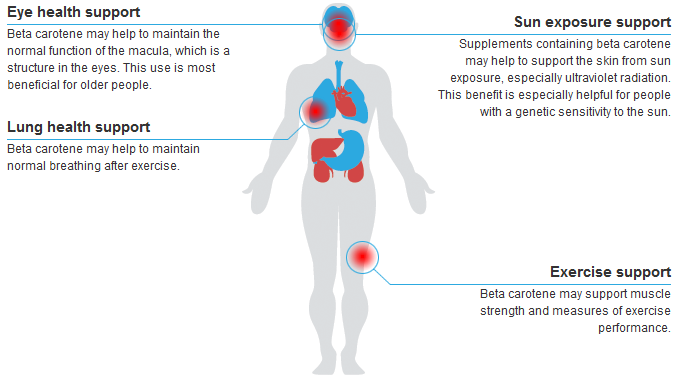
1. Supports Eye Health
As both an antioxidant and vitamin A source, beta-carotene protects the eyes against oxidative stress and contributes to healthy vision.
2. Boosts Skin Protection
Its antioxidant activity reduces free-radical damage from UV exposure, promoting healthier, younger-looking skin.
3. Strengthens Immunity
By converting into vitamin A, beta-carotene supports immune defense mechanisms, helping the body fight infections.
4. Promotes Heart Health
Some studies suggest that beta-carotene’s antioxidant properties may help lower oxidative stress in blood vessels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
5. Slows Cognitive Decline
There’s growing evidence that antioxidant-rich diets, including beta-carotene, may reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s.
Can You Have Too Much Beta-Carotene?
Unlike vitamin A supplements, beta-carotene from food is generally safe because the body regulates conversion. However, very high supplement doses can lead to carotenemia, a harmless condition where the skin turns yellow-orange.
For smokers and heavy drinkers, high-dose beta-carotene supplements are not recommended due to increased health risks shown in studies.
Conclusion
So, is beta-carotene an antioxidant? Yes—absolutely. Beta-carotene is a potent antioxidant that plays a protective role against oxidative stress, while also serving as a vital precursor to vitamin A. Together, these functions support vision, skin health, immunity, and overall wellness.
The best way to enjoy its benefits is by eating a diet rich in colorful fruits and vegetables, ensuring a natural balance of nutrients and antioxidants. Supplements may have their place in specific cases, but for most people, nature’s palette of beta-carotene-rich foods is the healthiest and safest choice.
Send Inquiry
Related Industry Knowledge
- Stevia سكر
- Algae Omega 3 Capsules and Liquid Benefits
- Moringa Powder: Organic, Raw, and Pure
- Benefits of the Milk Thistle to Liver
- Natural Distilled and Pure MSM Powder
- Organic Turmeric Root Powder Natural Benefits
- is magnesium taurate good for high blood pressure?
- Does fucoxanthin help you lose weight?
- What Are Anthocyanins? A Deep Dive into Nature's Vibrant Pigments
- What Happens To Your Body After Taking Creatine For 30 Days?