What does beta carotene do?
In the world of nutrition, beauty, and health science, few compounds capture as much attention as beta-carotene. Known for giving carrots, pumpkins, sweet potatoes, and other fruits and vegetables their vivid orange hue, beta-carotene is much more than a natural pigment. It is a powerful antioxidant and a provitamin A carotenoid, which means that the body can convert it into vitamin A when needed.
But what exactly does beta-carotene do in the body? And why is it a vital nutrient for both wellness and industry applications? This article dives deep into the science, health benefits, cosmetic applications, and industrial uses of beta-carotene, showing why it remains one of the most versatile and beneficial compounds in human health and nutrition.
What is Beta-Carotene?
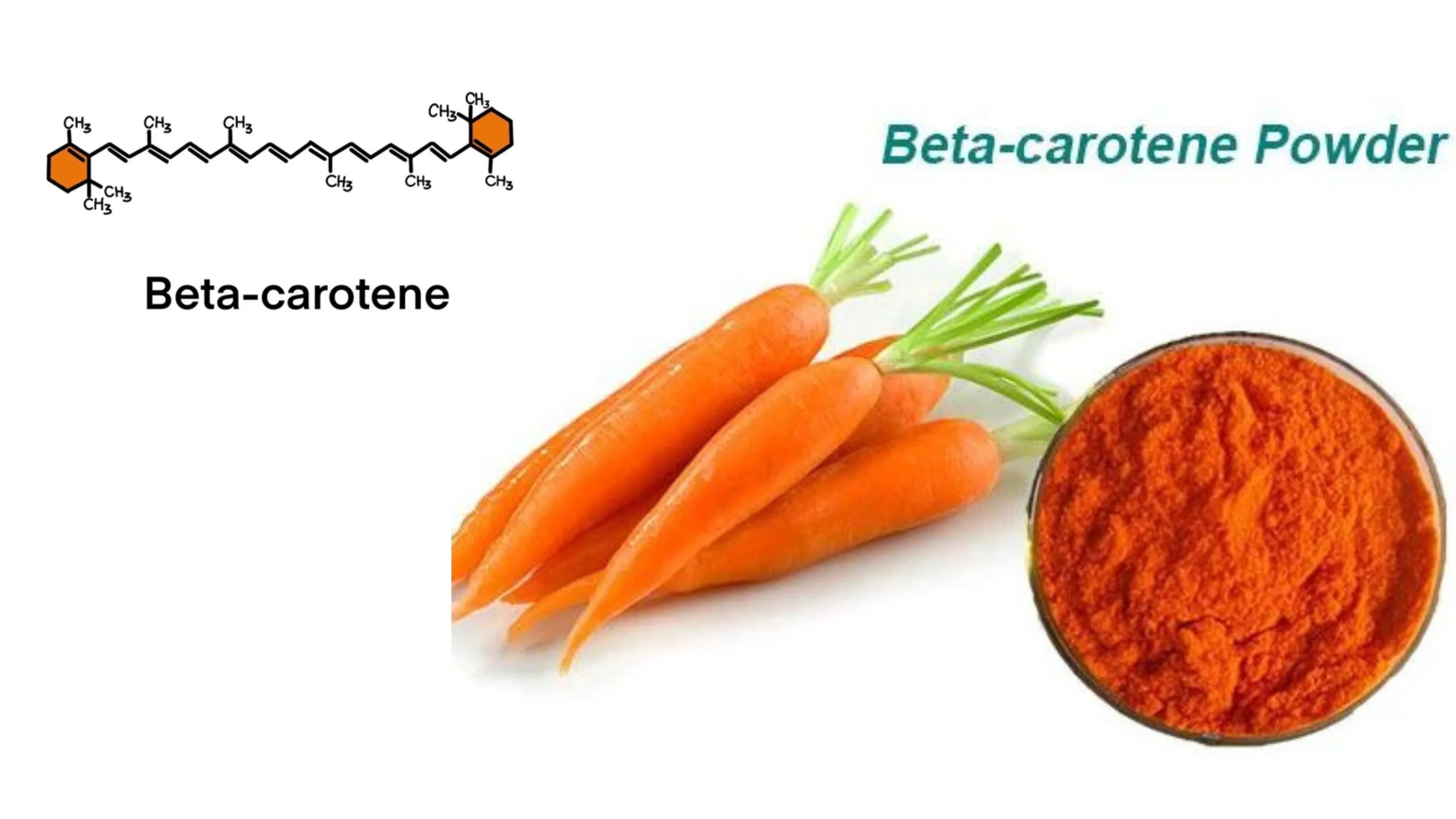
This element is an isomer of carotene, a pigment of both plant and animal origin that, when assimilated in the body, becomes vitamin A. It has a characteristic orange, yellow, or red color, which is precisely what gives those tones to the foods that contain it. That’s why carrots, for example, are orange. And, in fact, they are one of the vegetables with the highest beta-carotene content.
These natural antioxidants help protect the skin from the effects of the sun. They can create a natural filter against UV rays to protect the skin from sunburn. It is the vitamin A it produces that stimulates melanin production and promotes the proper functioning of skin cells.
However, beta-carotene also helps to strengthen the immune system and protect it against various types of diseases. And not only that, it also stimulates the production of white blood cells. Although the most common way to obtain it is through food, if a patient has trouble metabolizing or absorbing it, there are dietary supplements (in tablets or capsules) that can be used.
Recent research highlights the importance of considering the interaction between phytochemicals and other substances in the human body. It has been observed that their combination and chemical relationships are essential for the process to be effective. This means that phytochemicals present in fruits and vegetables are more effective in the body when they act in their natural form, synergistically combined with other compounds.
Carotenoids, for their part, when synergistically combined with other phytochemicals such as polyphenols and vitamin E, can inhibit the growth of cancer cells and offer protection against chronic diseases. That is why beta-carotene is at the forefront of recent research.
Molecular role: Beta-carotene is a lipophilic (fat-soluble) compound, stored in body fat and within cell membranes, where it protects lipids from oxidative stress.
Nutritional importance: Unlike preformed vitamin A (retinol), which can become toxic at high intakes, beta-carotene is safely converted by the body based on need.
This safety and multifunctionality make beta-carotene both unique and highly valuable.
What Does Beta-Carotene Do in the Body?
Beta-carotene has a variety of health benefits for many of the body’s systems. From protecting the lungs to improving cognitive function, beta-carotene has a wide range of health-improving qualities.
Eye Health
Provitamin A carotenoid beta-carotene may help prevent the onset of eye disease and can help promote good eye health.
Research shows that a diet high in beta-carotene and other carotenoids may reduce the risk of developing age-related macular degeneration (AMD) by up to 35%. That is particularly true for smokers who are at increased risk of vision loss due to AMD.
Beta-carotene also helps to improve eye health by keeping the cornea—the surface of the eye—healthy and moist. Vitamin A may help improve night vision or low light vision due to its ability to help the eye convert light into a signal sent to the brain.
As a powerful antioxidant, beta-carotene helps reduce the oxidative stress on our eyes caused by exposure to blue light from device screens and UV radiation. By boosting the immune system, vitamin A helps decrease eye inflammation and the risk of developing eye infections.
Immune Health
Because beta-carotene is an antioxidant, it can increase our immune health by reducing oxidative stress in the body. Oxidative stress directly contributes to chronic illnesses, including heart disease, arthritis, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes, stroke, atherosclerosis, and more.
Antioxidants boost our immune function by scavenging and destroying free radicals. Free radicals cause damage to our tissues, thereby contributing to chronic inflammation and disease formation. Researchers have shown beta-carotene to increase the activity and quantity of immune cells.
Carotenoids like beta-carotene have been linked to gene regulation and angiogenesis, or the growth and development of new blood vessels, affecting immune function.
Skin Health
Primarily attributed to its function as an antioxidant, beta-carotene can help improve skin health and appearance.
Studies show a diet rich in phytochemicals such as beta-carotene helps improve the skin’s defense against UV radiation from the sun. This protection will help the skin maintain its elasticity and decrease the effects of sun damage, including fine lines, wrinkles, and sunspots.
Beta-carotene’s effects may help prevent acne and reduce skin blemishes. It also has a natural exfoliation ability by promoting cell turnover, improving your skin’s health and appearance.
If having a natural tan is your goal, eating foods high in beta-carotene can increase skin pigmentation. Foods high in beta-carotene include dark leafy green vegetables like kale and spinach, cantaloupe, butternut squash, carrots, sweet potatoes, red and yellow peppers, and apricots. Herbs such as paprika, parsley, sage, cilantro, and coriander are also good sources of beta-carotene.
Because carotenoids are fat-soluble, adding an oil like olive or grapeseed oil, eating fatty fish like salmon, or eating nuts and seeds with these foods can help you better absorb the beta-carotene in your diet.
Lung Health
Studies suggest that a diet rich in beta-carotene is beneficial to lung health. Beta-carotene gets converted to vitamin A in the body, which helps with proper lung function.
Due to its involvement in maintaining epithelial cells, or cells in the linings of tissues, vitamin A is vital for a healthy respiratory tract. Vitamin A deficiency during pregnancy can have long-term adverse effects on the offspring’s lung health.
Vitamin A deficiency, along with protein malnutrition, is the most common nutritional disorder in the world. While this mainly affects children in developing countries, more than 20% of the population in the developed world gets less than two-thirds of the recommended intake of vitamin A. Both liver and plasma levels are below the accepted normal range in this 20% due to modern society’s habits of eating foods with poor nutritional value.
Vitamin A deficiency increases the risk of developing and dying from various infections and developing respiratory tract illnesses. Taking beta-carotene supplements can help elevate vitamin A levels safely without the risk of vitamin A toxicity.
Mental Health
Beta-carotene may improve mental health, including cognitive function and memory, thanks to its antioxidant status.
A series of studies found that long-term beta-carotene supplementation improved both memory and cognitive function. Other studies show that antioxidant supplementation remains useful in patients with stress-induced psychiatric disorders, including anxiety and depression.
Additional research demonstrates beta-carotene has antidepressant-like activity in stressed mice. Another study found that long-term beta-carotene supplementation for 15 years or longer may help prevent cognitive decline in men.
Acts as a Natural Colorant
Beyond health, beta-carotene is used as a natural food and cosmetic coloring agent. Its bright orange-yellow hue makes it an attractive alternative to synthetic dyes, aligning with consumer demand for clean-label products.
Industrial Applications of Beta-Carotene
Beta-carotene’s unique properties make it a valuable ingredient in several industries:
1. Food & Beverage Industry
Used as a colorant in juices, dairy products, margarine, and baked goods.
Marketed as a nutritional enhancer, especially in fortified foods.
2. Dietary Supplements
Available in capsules, soft gels, and powders.
Promoted for eye health, skin health, and antioxidant protection.
3. Cosmetics & Personal Care
Incorporated into creams, serums, lotions, shampoos, and lipsticks.
Provides both antioxidant support and natural pigmentation.
4. Animal Feed Industry
Added to animal feed to enhance the nutritional value and improve pigmentation of products like egg yolks and fish flesh.
Safety of Beta-Carotene
From Whole Foods
Beta-carotene from natural food sources is safe and highly beneficial. The body regulates how much it converts into vitamin A, preventing toxicity.
From Supplements
While supplements are safe for most people, high doses are not recommended for smokers, as some studies show increased lung cancer risk in this group.
Excessive intake may cause carotenemia, a harmless condition where the skin turns yellow-orange.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Supplements-You-Shouldnt-Be-Taking-for-Heart-Health-7b67c52b11a5488bb9392013d37c7327.jpg)
Conclusion
So, what does beta-carotene do? The answer is—a lot. From protecting the body against oxidative stress and supporting vision to enhancing skin radiance and contributing to heart and brain health, beta-carotene is a true powerhouse nutrient. Its multifunctional roles make it indispensable not only in human health but also across food, cosmetic, and pharmaceutical industries.
Whether consumed through colorful vegetables or incorporated into supplements and cosmetics, beta-carotene continues to prove its worth as one of nature’s most valuable compounds.
At Yangge Biotech, we specialize in producing and supplying high-quality beta-carotene and other natural ingredients for the food, cosmetic, pharmaceutical, and nutraceutical industries. Our products are manufactured with strict quality control and advanced technology to ensure purity, stability, and bioavailability.
Whether you’re formulating a skin-brightening cream, a nutritional supplement, or a functional beverage, Yangge Biotech provides the reliable sourcing and technical expertise to help your brand succeed.
📩 Contact us today to learn more about our beta-carotene solutions and how we can support your next product innovation.
Send Inquiry
Related Industry Knowledge
- Is Hemp Seed Protein Beneficial for You?
- NMN Powder: A Must-Have for Your Wellness Routine
- Unlocking the Benefits of NMN Powder for Longevity
- Where to buy soy lecithin?
- Psyllium Husk Powder: Best Natural Food
- Pure Resveratrol Powder for Skin Health
- is vitamin a same as beta carotene?
- hemp protein powder benefits and risks
- How can you benefits from almond protein powder?
- marigold flower extract uses for hair