What Do Antioxidants Do for the Body?
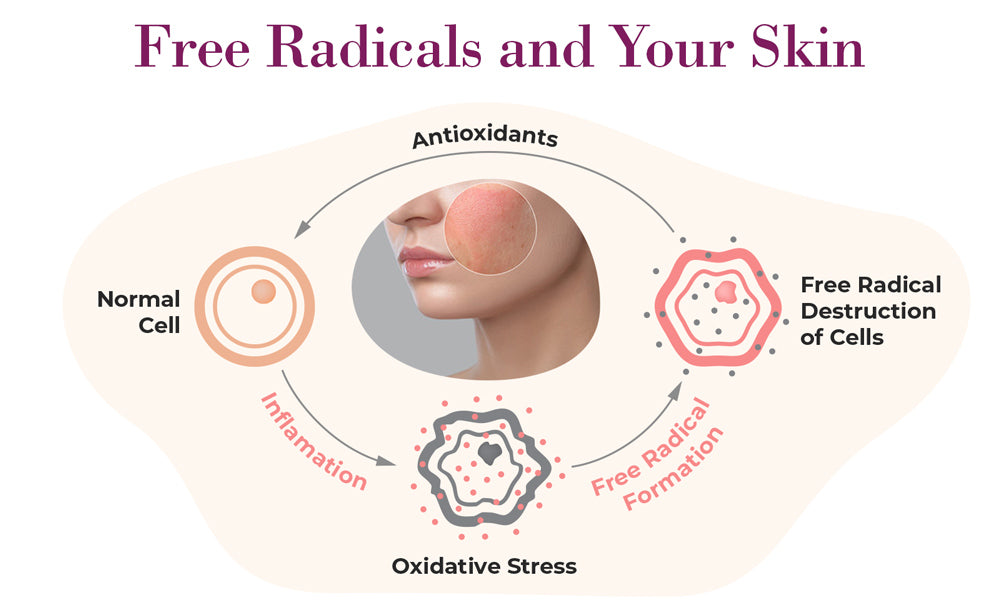
Every day, the human body is exposed to harmful substances known as free radicals—unstable molecules generated by environmental factors like pollution, UV rays, smoking, processed foods, and even the body’s own metabolic processes. Left unchecked, these molecules can cause oxidative stress, a process that damages cells, proteins, and DNA, contributing to aging and many chronic diseases.
This is where antioxidants come into play. These compounds help protect the body by neutralizing free radicals, reducing oxidative damage, and supporting overall health and longevity. From boosting immunity to promoting skin health and supporting brain function, antioxidants play a central role in maintaining wellness.
What Are Antioxidants?
Antioxidants are molecules that safely interact with free radicals, stopping the chain reaction before vital molecules are damaged. The body naturally produces some antioxidants (endogenous), but many must be obtained from diet or supplements (exogenous). These include vitamins, minerals, and a wide range of plant-based compounds such as polyphenols, flavonoids, and carotenoids.
Without sufficient antioxidants, free radicals can overwhelm the body's defense systems. Over time, this imbalance contributes to cellular aging and increases the risk of diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative conditions.

Antioxidants are thought to work in concert with one another, forming what is known as the antioxidant network. An example of the antioxidant network is shown below. Alpha-tocopherol (major form of vitamin E in our body) is oxidized, forming an alpha-tocopherol radical. This donation of an electron stabilizes reactive oxygen species. Ascorbate (vitamin C) is then oxidized, forming dehydroascorbate to regenerate (reduce) alpha-tocopherol. Ascorbate is then regenerated by the selenoenzyme thioredoxin reductase. This demonstrates how antioxidants can function as a network to regenerate one another so they can continue to function as antioxidants.

Figure.1 The theorized antioxidant network
Common antioxidants include vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and astaxanthin, lycopene green tea extract, PQQ powder, NMN powder, AKG powder, and other plant-based foods. Consuming antioxidant-rich foods is believed to promote health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
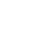
How Do Antioxidants Work
Everyday our body tries to cope with stress. Externally, we deal with environmental stressors like pollution while internally, we face physical and emotional stresses. High levels of stress release large amounts of free radicals in our body. Under normal circumstances, the body neutralizes free radicals on its own. However, with persistent stress from our busy lifestyles, free radicals can become too much for the body to handle.

Free radicals are unstable molecules that cause oxidative stress, that can lead to cell and tissue damage, which experts believe is a major precursor to chronic diseases and premature aging.
Antioxidants are known as “free radical scavengers” since they neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in the body caused by these unstable molecules.
Antioxidant Benefits
1. Protecting Cells from Oxidative Damage
The core function of antioxidants is to protect cells from damage caused by oxidative stress. This includes maintaining the integrity of cell membranes, preserving DNA structure, and preventing inflammation—factors that are central to long-term health.
2. Supporting Immune Function
Certain antioxidants—like vitamin C, green tea polyphenols, and astaxanthin—have immune-modulating effects. They help white blood cells function effectively and reduce chronic inflammation, which is often associated with immune dysfunction.
3. Slowing the Aging Process
Oxidative stress is a major contributor to visible signs of aging, such as wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots, as well as internal aging processes that affect energy, cognition, and organ function. Antioxidants slow these processes by repairing and protecting tissue at the cellular level.
4. Enhancing Brain Health
The brain is highly vulnerable to oxidative stress due to its high oxygen use and lipid content. Antioxidants like NMN, PQQ, and green tea extract help protect neurons, improve mitochondrial function, and enhance cognitive performance, potentially reducing the risk of Alzheimer’s and other neurological disorders.
5. Promoting Heart Health
Oxidative stress can damage blood vessels, oxidize LDL cholesterol, and contribute to the development of atherosclerosis. Antioxidants reduce these risks by improving endothelial function, decreasing inflammation, and preventing plaque buildup in the arteries.
6. Improving Skin Health
Many antioxidants are known for their skin-protective properties. They reduce the impact of UV rays, improve collagen production, hydrate the skin, and reduce inflammation, which helps prevent conditions like acne and eczema.



What Do Antioxidant Smoothies Do To Us?
We wanted to find out whether drinking a smoothie high in antioxidants had any effect on the antioxidant levels in the body.
Ten healthy volunteers (BMI between 18.5-30) were asked to avoid foods containing antioxidants for 48 hours before the experiment started and for 24 hours afterwards. This included fruit, vegetables and whole grain products, coffee and tea, beer and wine.
Each volunteer was asked to drink 360 mls of a smoothie that was advertised as being rich in antioxidants.
A blood sample was taken before the experiment and then at intervals for 24 hours. Each sample was analysed for antioxidant concentration and for blood sugar levels.
A urine sample was also taken before and after the experiment started.
The results
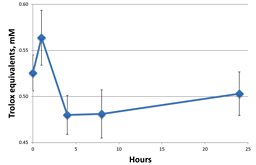
Plasma TEAC
After an initial rise in the antioxidant status after one hour, the concentrations then fell below the baseline. By the time the experiment had finished (24 hours), the level of antioxidants in the volunteers’ blood was only just back to normal.
The urine samples showed no significant change in the level of antioxidants.
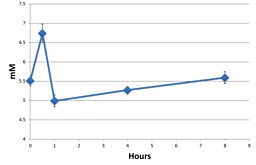
Plasma glucose
What Do Antioxidants Do For Skin?
Gobbling up free radicals is great — but what exactly does that mean for your skin health? Here’s the highlight reel of antioxidant skin benefits:
1. Sun Damage Repair: One of the quickest ways you can compromise the integrity of your skin is through radiation. Most commonly, this means exposure to ultraviolet rays from too much direct and unprotected access to sunlight. With antioxidants, you can halt and reverse damage done by free radicals by stimulating circulation, which encourages new cell growth.
2. Wrinkles: Antioxidant vitamins C and E are excellent for reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. These vitamins help to plump your skin, soften wrinkles, and bestow a more youthful appearance to the skin.
3. Elasticity: As you undergo the aging process, your skin begins to lose elasticity over time, resulting in a loss of firmness. Antioxidants like CoQ-10 help reduce and even prevent these common signs of aging.
4. Inflammation; Inflammation is the root of many common skin issues, including acne, redness, uneven skin tone, and wrinkles. Antioxidants calm inflammation by boosting cell metabolism and increasing circulation.
Here are some of our favorite skin-loving antioxidants that can be found in skin, body and personal care products.
1. Vitamin E (tocopherol) – protects the skin from free radicals like pollution or UV from damaging healthy skin cells. Many oils and plants contain natural vitamin E, the form that the body can most easily recognize and make use of its benefits.
2. Green Tea – Is one of the most well-researched antioxidants. It is said to contain the most potent components needed to neutralize free radicals. It’s ability to calm the look and feel of inflammation is what makes it such an important antioxidant for protecting cells, contributing to a younger-looking complexion and helping the body to fend itself from disease.
3. Grapeseed Oil – High in polyphenols, grapeseed oil binds with free radicals, stopping them from damaging healthy skin cells. Some studies show grapeseed benefits similar to the antioxidant protection provided by vitamin E and vitamin C.
4. Lycopene – This natural antioxidant also helps to fight inflammation and protects the skin from environmental pollutants that can harm the skin and cause breakouts.
How Do We Get Antioxidants?
Let’s take a deeper look at several powerful antioxidants and how they contribute to your health:
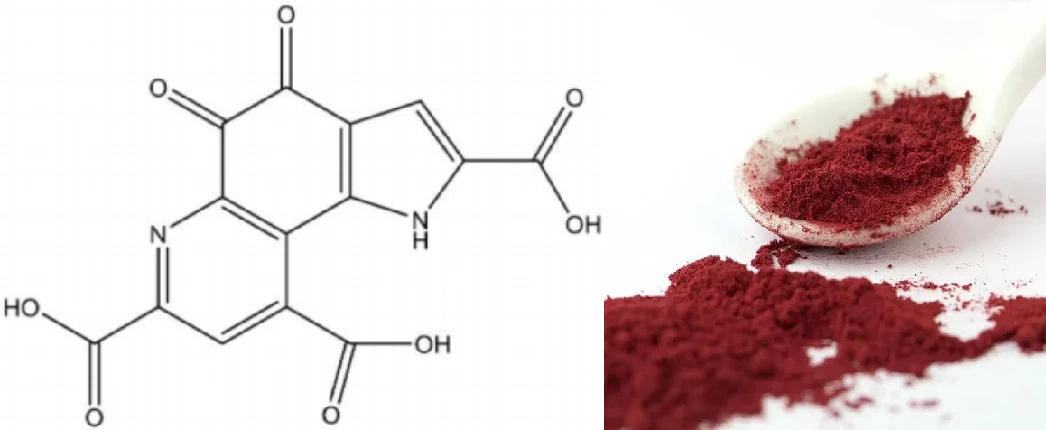
1. Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin is a red pigment found in microalgae and seafood like salmon and krill. It’s one of the most powerful natural antioxidants, with a unique ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and protect both the skin and internal organs.
Key Benefits:
Protects the skin from UV-induced damage
Improves elasticity and hydration
Reduces inflammation in the joints and muscles
Supports eye and brain health
Enhances endurance and recovery

2. Lycopene
Lycopene is a bright red carotenoid found primarily in tomatoes. It’s fat-soluble and best absorbed when consumed with oils.
Key Benefits:
Promotes prostate and cardiovascular health
Protects skin from photoaging
Lowers oxidative stress in blood vessels
Reduces the risk of certain types of cancer
Neutralizes singlet oxygen, a particularly harmful free radical

3. Green Tea Extract
Derived from the leaves of Camellia sinensis, green tea extract is rich in polyphenols, especially epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound.
Key Benefits:
Boosts metabolism and fat oxidation
Enhances immune defense
Protects neurons from oxidative damage
Reduces inflammation and improves skin health
Supports cardiovascular function by lowering LDL and improving blood flow

4. PQQ (Pyrroloquinoline Quinone)
PQQ is a lesser-known but incredibly effective antioxidant that plays a key role in mitochondrial biogenesis — the creation of new mitochondria within cells.
Key Benefits:
Boosts cellular energy production
Supports brain function and memory
Protects the heart and nerves from oxidative damage
Reduces inflammation
Stimulates mitochondrial repair and growth
5. NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide)
NMN is a precursor to NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), a vital coenzyme involved in DNA repair, energy metabolism, and gene expression. As we age, NAD+ levels decline, making NMN supplementation an important tool in anti-aging science.
Key Benefits:
Increases energy levels
Improves insulin sensitivity and metabolism
Slows cellular aging
Enhances brain function
Protects cardiovascular health
6. AKG (Alpha-Ketoglutarate)
Alpha-Ketoglutarate is a key molecule in the citric acid cycle, essential for energy production. It also plays roles in amino acid metabolism and detoxification.
Key Benefits:
Supports muscle recovery and strength
Reduces age-related bone loss
Improves nitrogen balance in the body
Promotes cellular longevity
May delay biological aging processes

When To Consider Antioxidant Supplements
Oral or topical antioxidant supplements can be prescribed to patients who don’t get enough of them through their diet or people suffering from oxidative stress. Following are certain cases which would permit the use of antioxidant supplements:
1. Lack of appropriate dietary intake: Antioxidant supplements may be helpful for people who do not have easy access to vegetables and fruits or who have harsh metabolic requirements.
2. Existing Medical Conditions: Certain chronic illnesses like macular degeneration might need oral antioxidant supplements based on a patient’s clinical management plan.
3. Environmental and lifestyle extremes: Patients smoking, people who are suffering from immense environmental pollution, or recovering from a major illness or surgery might be permitted to use supplementation.

Conclusion
Antioxidants are essential defenders against the damaging effects of free radicals. By neutralizing these unstable molecules, antioxidants support nearly every system in the body—from the immune system and skin to the brain and heart. While the body produces some antioxidants naturally, supplementing with potent sources like astaxanthin, lycopene, green tea extract, PQQ, NMN, and AKG can provide targeted support, especially under stress or aging-related decline.
Incorporating antioxidant-rich foods and supplements into your daily routine may not just protect your health—it can help you feel and function better at every stage of life.
Contact us today to request samples, COAs, or wholesale pricing. We offer high-quality antioxidant ingredients including Astaxanthin, Lycopene, Green Tea Extract, PQQ Powder, NMN Powder, and AKG Powder—perfect for your health and wellness formulations. Email: Info@yanggebiotech.com
References & Links
Gropper SS, Smith JL, Groff JL. (2008) Advanced nutrition and human metabolism. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Publishing.
Packer L, Weber SU, Rimbach G. (2001) Molecular aspects of alpha-tocotrienol antioxidant action and cell signalling. J Nutr 131(2): 369S-373S.
Antioxidants. (2018, March 1)
https://medlineplus.gov/antioxidants.html
Antioxidants and cancer prevention. (2017, February 6)
https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/diet/antioxidants-fact-sheet
Antioxidants: Beyond the hype. (n.d.)
https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/antioxidants/
Antioxidants: In depth. (2016, May 4)
https://nccih.nih.gov/health/antioxidants/introduction.htm
Antioxidants: What you need to know. (2017, February 15)
https://familydoctor.org/antioxidants-what-you-need-to-know/
Lobo, V., Patil, A., Phatak, A., & Chandra, N. (2010, July-December). Free radicals, antioxidants, and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacognosy Review, 4(8), 118-126
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3249911/
Send Inquiry
Related Industry Knowledge
- What is Guarana and What are its Properties and Benefits?
- Chlorophyll and Its Impact on Mental Well-being
- Does beta carotene cause cancer
- Algae Omega 3 Capsules and Liquid Benefits
- Natural Garlic Tablets: Benefits and Uses
- Uses and Benefits of Pure Capsaicin
- Pure Psyllium Husk Powder Health Benefits
- Does instant white tea have any health benefits?
- Benefits and Uses of Natural Food Coloring
- 2024 Global Food Color Market Report- Trends, Forecast, And Competitive Analysis - YANGGEBIOTECH