Amylase Enzyme Function
Amylase enzymes, those remarkable catalysts that play a key role in breaking down complex carbohydrates, are not limited to just our digestive systems. Their versatility extends into various industries and scientific fields, where they are harnessed for a wide range of applications. Let's delve into the fascinating world of amylase enzyme applications, where science meets innovation.
Amylase Enzyme Food Industry: Baking and Brewing Marvels
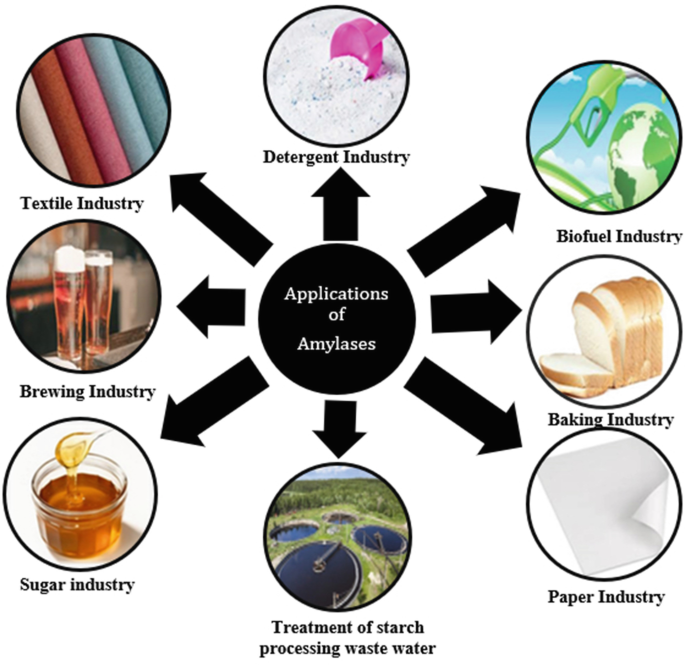
The food industry has long embraced the power of amylase enzymes. In baking, amylases are employed to improve the texture and quality of baked goods. By breaking down starches into simpler sugars, they enhance the dough's elasticity and contribute to a lighter, fluffier texture in bread and pastries. Similarly, in brewing, amylases play a pivotal role in converting starches from malted grains into fermentable sugars, which yeast then convert into alcohol during the brewing process.
Abstract:
Frozen bread doughs usually exhibit less bread volume and poor texture due to dough weakening as well as reduced yeast viability. The objectives of this study were to improve the textural properties of frozen bread dough by applying carbohydrate-active enzymes, α-amylase and endo-xylanase. Each enzyme was applied to dough formulation at 20 (748 and 3.5 units, respectively) and 100 ppm levels of flour, and their combined treatments were also applied. Enzyme-treated doughs were kept frozen at −20 °C for 2 weeks, and then baked following the official American Association of Cereal Chemists (AACC) method. A texture profile analysis of oven-baked breads was performed at 25 °C after a 5-day storage period. α-Amylase treatment at a 100 ppm level increased the specific bread volume by 24.5% and 21.9% when compared to untreated fresh and frozen bread doughs, respectively, and decreased crumb hardness by 63.4% and 58.3%; endo-xylanase (100 ppm) also decreased crumb hardness by 56.9% and 26.9%. The combined use of α-amylase and endo-xylanase retarded bread hardening synergistically after a 5-day storage period.

Amylase Enzyme Textile Manufacturing: Fabric Desizing
In the textile industry, amylase enzymes find their way into fabric desizing processes. Desizing refers to the removal of starch from fabrics after weaving, which is crucial for subsequent dyeing and finishing processes. Amylases effectively break down the starch, making it easier to remove from the fabric's surface. This enzymatic approach not only improves the efficiency of desizing but also contributes to a more eco-friendly textile production process.
Amylase Enzyme Paper Industry: Enhancing Recycled Paper
Amylase enzymes play a role in the paper recycling process. When recycling paper, ink needs to be removed to produce clean, high-quality paper products. Amylases assist in breaking down the starch-based ink particles, helping to detach them from the paper fibers. This enzymatic deinking process is considered environmentally friendly compared to traditional chemical methods and contributes to the sustainability of the paper industry.
Amylase Enzyme Biofuel Production: A Sustainable Future
In the pursuit of sustainable energy sources, amylase enzymes have found a place in biofuel production. Biomass, such as corn and wheat, contains starch that can be converted into biofuels like ethanol. Amylases play a crucial role in breaking down the starches into fermentable sugars, which can then be converted by microorganisms into ethanol through fermentation. This application highlights the potential of amylase enzymes in contributing to a greener energy landscape.
Amylase Enzyme Medical Diagnostics: Monitoring Pancreatic Health
Beyond industrial applications, amylase enzymes have medical implications. Elevated levels of amylase in the blood can be indicative of pancreatic disorders such as pancreatitis. Medical professionals utilize amylase testing to diagnose and monitor these conditions. The measurement of amylase levels aids in assessing pancreatic function and identifying potential health issues.
Amylase Enzyme Detergent Industry: Enzymatic Stain Removal
Enzymatic stain removers in laundry detergents often contain amylase enzymes. These enzymes target starch-based stains, such as those from food spills, sauces, or baby food. By breaking down the starch molecules in the stains, amylase enzymes help to effectively remove stubborn marks from clothing, contributing to the effectiveness of modern laundry care products.
Amylase Enzyme Pet Food Industry: Enhancing Digestibility for Pets
Just like humans, our pets rely on the breakdown of carbohydrates for energy and nutrition. However, the digestive systems of dogs and cats differ from ours, and their ability to process certain carbohydrates can be limited. Enter amylase enzymes. By incorporating amylases into pet food formulations, manufacturers can mimic the natural digestive process, breaking down complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars that pets can readily absorb. This enhances the overall digestibility of the food and ensures optimal nutrient absorption.
WHY CHOOSE YANGGE BIOTECH?
YANGGE BIOTECH has been committed to the production and export of standardized extracts and nutritional fine chemicals to meet the needs of the global food and beverage, dietary supplements and cosmeceutical industries. All of the products at YANGGE BIOTECH INGREDIENTS are produced in a facility that is certified in the GMP Safe Food Certification Program. Contact us by email: info@yanggebiotech.com
Conclusion
In essence, amylase enzymes are a prime example of how nature's biochemical wonders can be harnessed to benefit various aspects of human life. From enhancing the quality of our daily bread to revolutionizing textile manufacturing and contributing to sustainable energy solutions, these enzymes demonstrate their remarkable versatility and impact across industries and scientific domains.
References:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32491670/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6825871/
https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/amylase-test/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557738/
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=167&contentid=amylase_blood
Send Inquiry
Related Industry Knowledge
- Is soy lecithin bad for you
- Cistanche Benefits
- Beetroot Red Powder: A Natural Food Dye Alternative
- What is Glutathione and Why Do We Need it?
- Organic Sunflower Lecithin for Breastfeeding
- What Can Apple Cider Vinegar Tablets Target
- Boost Your Nutrition with Organic Rice Protein Powder – Here’s Why
- Sorghum Flour: The Gluten-Free Recipe
- The BEST Way To Use Creatine For Muscle Growth (4 STEPS)
- What Are Exosomes Used for In Skincare