is lion's mane mushroom good for your brain
In today’s fast-paced world, maintaining optimal cognitive function and mental well-being is paramount. From managing hectic schedules and long commutes, to balancing various responsibilities, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed and mentally drained.
Thankfully, at fourfive we’ve found the answer to upping your game when it comes to mental clarity and focus. Our Lion’s Mane Mushroom powder has been designed for its array of health benefits and brain power properties.
What is Lion’s Mane Mushroom?
Lion’s mane mushroom (Hericium erinaceus) is a distinctive, shaggy, white fungus resembling a lion’s mane, traditionally used in East Asian herbalism for its potential benefits to brain and gut health.
Known for its mild, sweet, seafood-like flavor and meaty texture, it is both a culinary delicacy and a popular nootropic supplement for enhancing cognitive function and emotional well-being.
Lion’s mane mushroom grows naturally on hardwood trees such as oak, beech, and maple, often found on decaying or dying wood in temperate forests across North America, Europe, and Asia. It thrives in shaded, moist environments, typically emerging in late summer through fall.

Lion’s Mane Mushroom Benefits:
Lion’s Mane Mushroom, scientifically known as Hericium erinaceus, has been used for centuries in traditional medicine for its neuro-protective properties. Rich in compounds like hericenones and erinacines, Lion’s Mane stimulates the production of nerve growth factor (NGF), essential for the growth, maintenance, and survival of neurons.
Several studies have demonstrated the cognitive benefits of Lion’s Mane Mushroom. For example, a study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry in 2009 found that Lion’s Mane extract significantly improved cognitive function in mice, suggesting its potential for human enhancement too.

The Relationship Between Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) and Cognition
Nerve growth factor (NGF) assists with the growth of nerve cells, or neurons, the basic cellular units of nervous tissue.
Along with BDNF (brain-derived neurotrophic factor), another key brain-building factor, NGF plays a key role in various cognitive functions such as memory and learning.
Specifically, Nerve Growth Factor (NGF) is involved in the following cognitive pathways:
Promotes growth, development, and survival of brain cells
Differentiates “blank” stem cells into specialized neurons
Organizes and maintains neurons throughout the nervous system
Regulates synaptic plasticity and other key structural activities related to memory and learning
Lion's mane mushrooms are most highly regarded for NGF support. When we look at NGF's far ranging impact on brain function, it's easy to see why Hericium erinaceus supplementation is rapidly gaining popularity.
Neural Regeneration: NGF promotes the growth and repair of neurons, helping to heal from cellular damage caused by aging and stress, as well as supporting brain injury recovery. These processes, including neurogenesis (creation of new brain cells) are key for nervous system health.
Neuroplasticity: By fostering the brain’s ability to form new neural connections, NGF enhances neuroplasticity, a key mechanism for learning, memory, and adapting to new experiences. This adaptability allows the brain to reorganize itself throughout life.

Cell-to-Cell Signaling: NGF improves communication between neurons, enabling efficient signaling that powers everything from basic sensory functions to complex cognitive tasks.
Brain Cell Replication: Healthy NGF levels encourage the replication of brain cells, replacing old or damaged neurons and maintaining cognitive reserves. This helps mental sharpness as we age.
Neuroprotection: NGF shields neurons from damage caused by inflammation, oxidative stress, and other harmful factors. This protective role is vital for preserving brain health and proactively addressing cognitive decline.
Age-Related Cognitive Decline: As people age, lower NGF levels are associated with mild cognitive impairment (MCI), a condition characterized by reduced memory and cognitive processing. MCI can serve as an early warning sign of more serious neurodegenerative problems.
By supporting NGF levels, Lion's Mane mushroom supplements and foods may help address these issues and promote brain health over time.

How to Use
You can find fresh and dried lion's mane mushrooms and lion's mane extracts in supplement stores and online. It is often part of a mushroom mix or blend of medicinal mushrooms, including reishi and chaga. There are no official guidelines for lion's mane supplementation. Most supplements will come with their own set of suggested directions for use.
Tea: Lion's mane tea can be found in loose-leaf, powder, or tea bag varieties.
Capsules: Lion's mane capsules or tablets are often marketed for enhancing focus,
Coffee: Lion's mane is an alternative to coffee due to its stimulating effects.
Powders: Lion's mane supplement powders can be added to smoothies or juices.
Tinctures: Tinctures are considered highly concentrated plant extracts and are often made through a process of alcohol extraction.
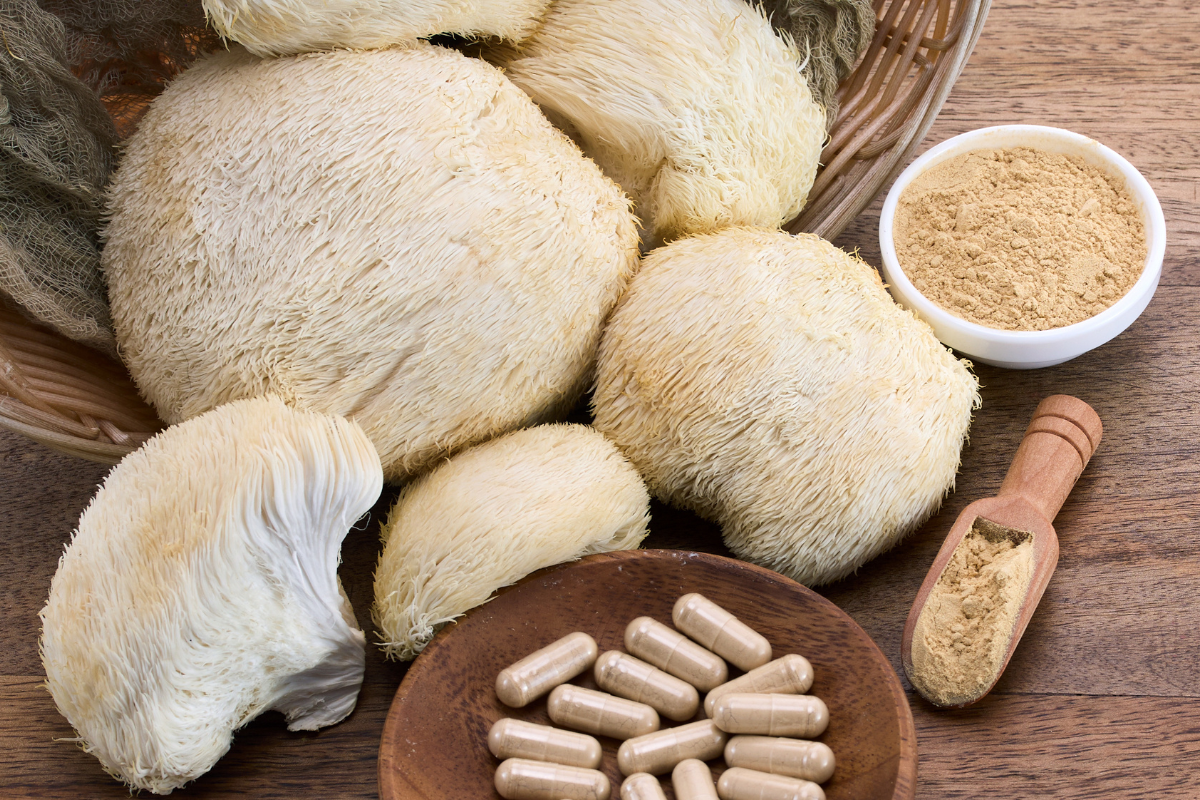

Lion's Mane Mushrooms Dosage Notes
How much Lion’s Mane should you take?And how much Lion's mane is too much? Let's do a quick rundown of lion's mane dosage ranges.
Lion’s mane supplements typically provide between 250 mg and 2,500 mg, depending on individual needs and desired effects.
Beginners can start with 500-1,000 mg per day to gauge tolerance and watch for side effects.
For nootropic benefits like improved focus, memory, mood, and brain health, a daily dose of 500-1,500 mg is often suggested.
Older adults managing mild cognitive decline may benefit from higher doses of 2,000-3,000 mg daily, as supported by some studies.
However, clinical trials are somewhat lacking on lion’s mane mushroom, so there is no definitive “best recommended” lion’s mane mushroom dosage yet.

Summary
Lion's mane mushroom has been a culinary staple and health-promoting herb in eastern traditions for thousands of years. With over 2,000+ fungus species used in traditional herbal health practices, most “medicinal mushrooms" are typically appreciated for their immune support benefits. However, Lion’s Mane mushroom is unique in that it seems to more directly improve brain health — and by that token: brain performance.
By stimulating nerve growth factor, Lion’s Mane mushroom powder base supplements help keep your nervous system structurally intact, well beyond the natural dip in NGF we all inevitably experience with age. In turn, lion's mane may help with memory deficits, brain fog, mood and other cognitive concerns. Beyond the brain, it may help with gut health, immune function and more.
References
Lai PL et al. Neurotrophic properties of the Lion’s mane medicinal mushroom, Hericium erinaceus (Higher Basidiomycetes) from Malaysia. Int J Med Mushrooms. 2013; 15(6): 539-54.
Mori K, Inatomi S, Ouchi K, Azumi Y, Tuchida T. Improving effects of the mushroom Yamabushitake (Hericium erinaceus) on mild cognitive impairment: a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytother Res. 2009 Mar;23(3):367-72. doi: 10.1002/ptr.2634. PMID: 18844328.
Nagano M, Shimizu K, Kondo R, Hayashi C, Sato D, Kitagawa K, Ohnuki K. Reduction of depression and anxiety by 4 weeks Hericium erinaceus intake. Biomed Res. 2010 Aug;31(4):231-7.
Chong PS, Fung ML, Wong KH, Lim LW. Therapeutic Potential of Hericium erinaceus for Depressive Disorder. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 25;21(1):163. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010163. PMID: 31881712; PMCID: PMC6982118.
Lee KF et al. Protective effects of Hericium erinaceus mycelium and its isolated erinacine A against ischemia-injury-induced neuronal cell death via the inhibition of iNOS/p38 MAPK and nitrotyrosine. Int J Mol Sci. 2014 Aug 27; 15(9): 15073-89.
Send Inquiry
Related Industry Knowledge
- Green Powder with Chlorophyll and Spirulina
- Beetroot Red Powder: A Natural Food Dye Alternative
- Best Glutamine Powder Health Benefits
- The Importance of Biotin for Healthy Hair
- Best Benefits of Acidophilus Capsules
- Turmeric with Black Pepper: Ginger Benefits
- Pure Collagen: Powder, Liquid, and Serum
- Marine Collagen Powder: The Peptide Effects
- how does tongkat ali increase testosterone?
- Is fish collagen good for skin?